A Geographic Overview: Understanding Indonesia’s Neighbours
A Geographic Overview: Understanding Indonesia’s Neighbours
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview: Understanding Indonesia’s Neighbours
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview: Understanding Indonesia’s Neighbours. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview: Understanding Indonesia’s Neighbours
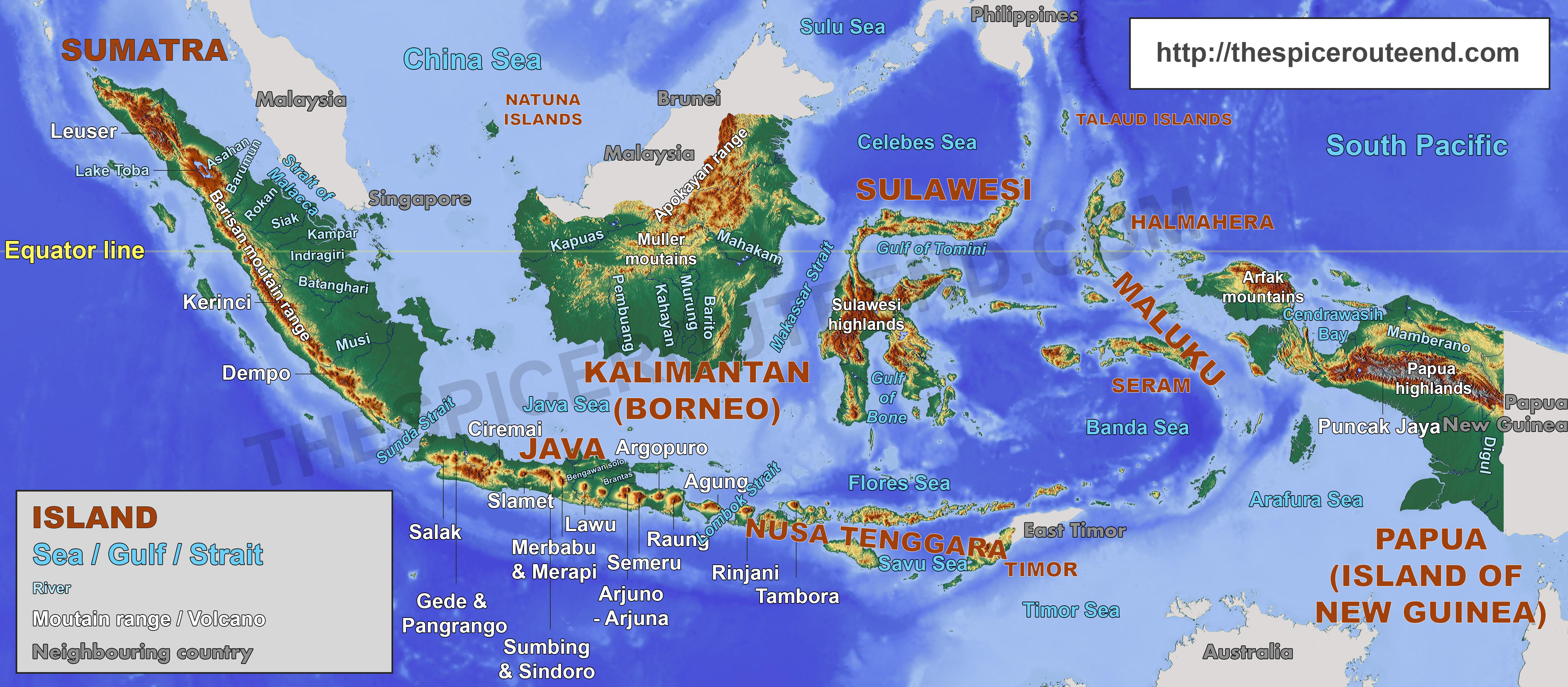
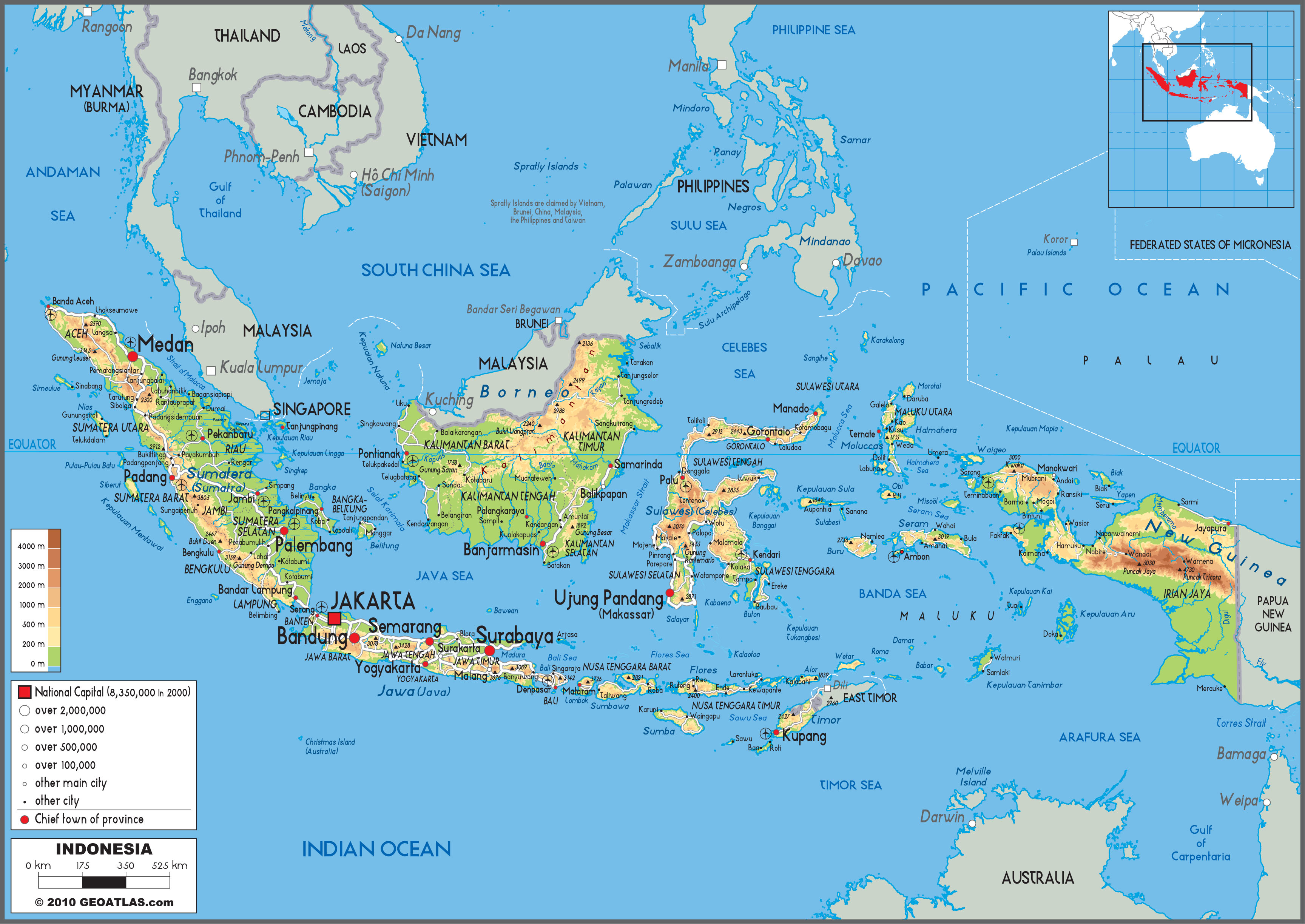
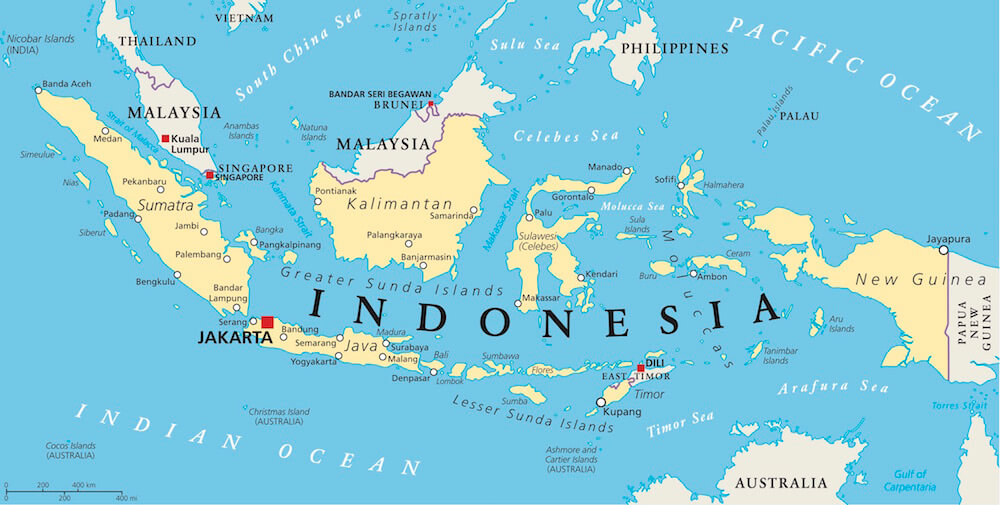
Indonesia, the world’s largest archipelago nation, occupies a strategically important position in Southeast Asia. Its proximity to numerous countries across the Malay Archipelago and the Asian mainland makes it a hub of cultural, economic, and political interaction. This article delves into the geographical landscape surrounding Indonesia, exploring the countries that share its borders and the significance of their relationships.
Southeast Asia’s Maritime Crossroads:
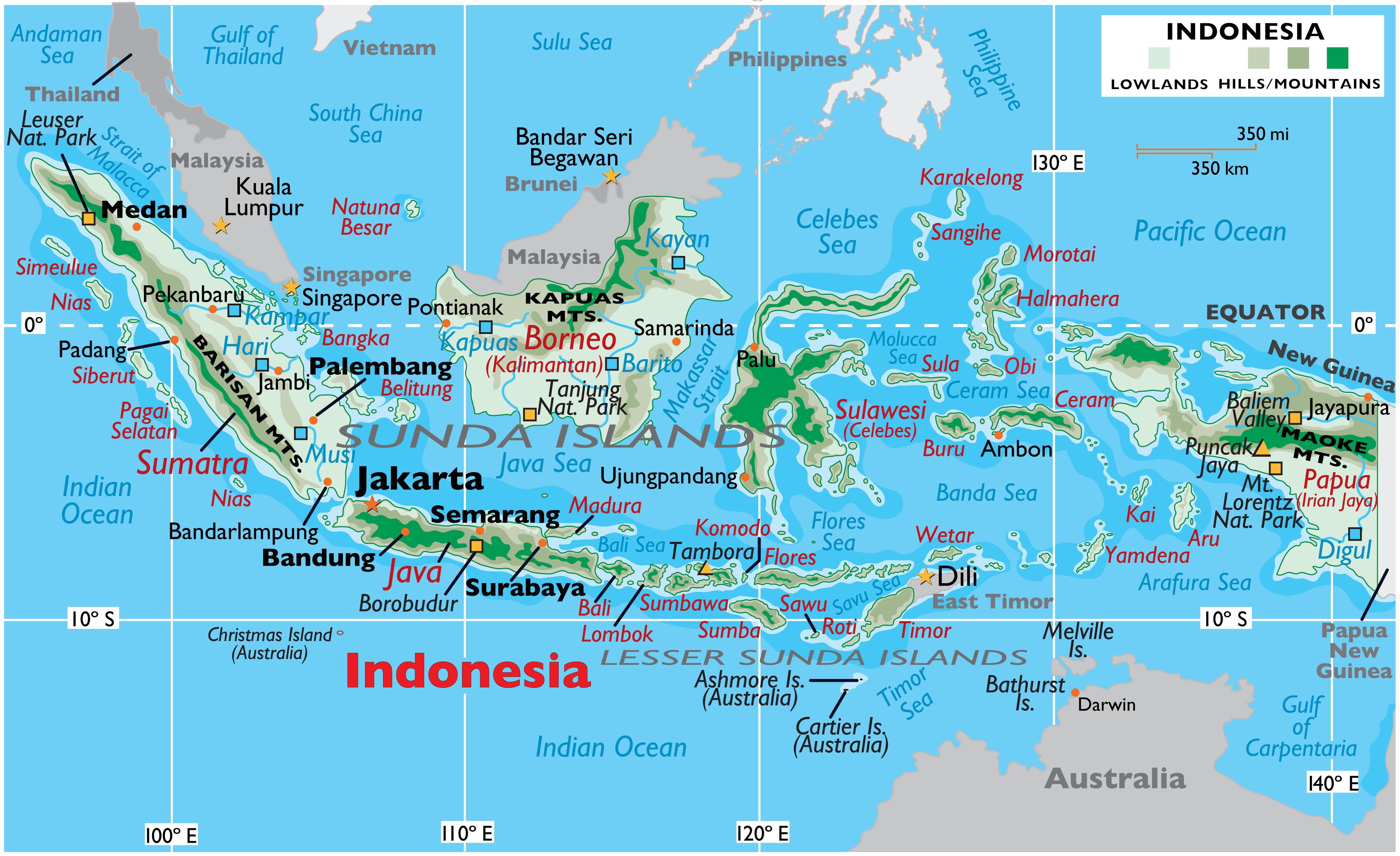
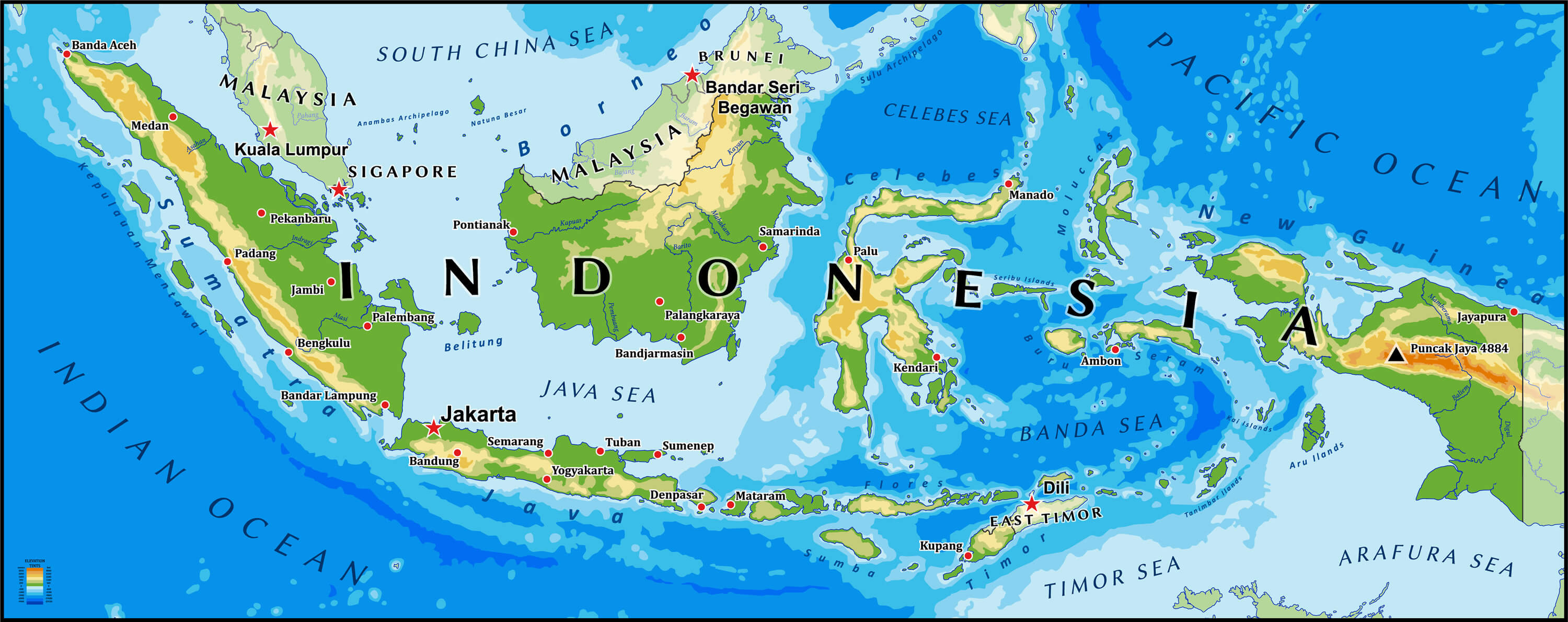
Indonesia’s geographic location, straddling the equator and nestled between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, has shaped its history and continues to influence its present. Its vast archipelago, comprising over 17,000 islands, stretches over 5,000 kilometers from east to west, encompassing a vast maritime domain. This strategic positioning has made Indonesia a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange for centuries.
The Neighbours:
Indonesia shares maritime borders with ten countries, each contributing to the complex tapestry of regional relations. These neighbours, clockwise from the west, are:
-
India: Situated across the Indian Ocean, India’s historical and cultural ties with Indonesia run deep. The two nations share a common heritage, with the spread of Hinduism and Buddhism from India influencing Indonesian culture. Today, India and Indonesia collaborate on various fronts, including trade, defence, and cultural exchange.
-
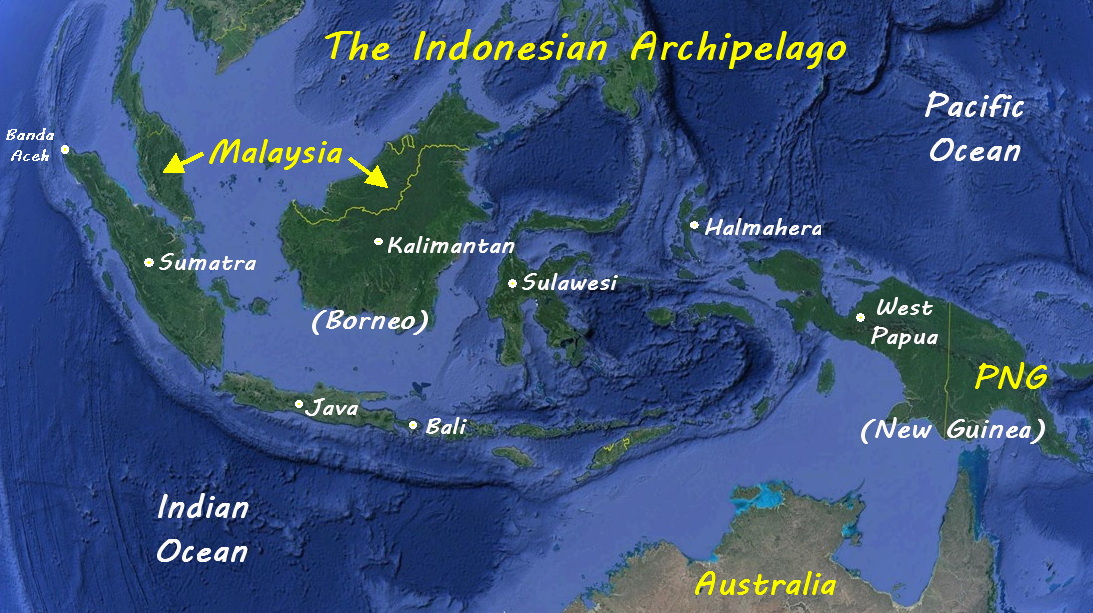
Malaysia: Sharing a long land border on the island of Borneo, Malaysia and Indonesia have a history intertwined by shared culture, language, and religion. The two countries face similar challenges, including environmental concerns and the need for regional cooperation.
-
Singapore: Situated at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, Singapore is a vital trading hub and a key partner for Indonesia. The two nations collaborate on economic development, trade, and regional security.
-
Brunei: Located on the northern coast of Borneo, Brunei shares a land border with Indonesia. The two countries have a strong historical and cultural connection, and their relationship is marked by cooperation in trade and development.
-
Philippines: Separated by the Celebes Sea, the Philippines and Indonesia share a cultural connection through their shared Malay ancestry. The two nations have strong economic ties and cooperate on regional security issues.
-
East Timor: Sharing a land border on the island of Timor, East Timor gained independence from Indonesia in 2002. The two countries have a complex relationship, marked by historical tensions but also by growing cooperation in trade and development.
-
Australia: Across the Timor Sea, Australia and Indonesia have a close relationship based on shared interests in regional security, trade, and environmental protection. The two countries collaborate on issues such as counter-terrorism, climate change, and maritime security.
-
Papua New Guinea: Located to the east of Indonesia, Papua New Guinea shares a land border with the Indonesian province of Papua. The two countries have a complex history, with the border region becoming a focus of separatist movements.
-
The Pacific Island Nations: Indonesia shares a maritime border with several Pacific Island nations, including Palau, Micronesia, and Kiribati. These relationships are primarily focused on regional cooperation and environmental protection.
-
Vietnam: Though not directly bordering Indonesia, Vietnam shares a maritime border with its neighbour, Malaysia, and plays a significant role in regional security and economic cooperation.
The Importance of Regional Relations:
Understanding the geographical context of Indonesia’s neighbours is crucial for appreciating the country’s role in Southeast Asia and beyond. The relationships between these nations are shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including:
-
Economic interdependence: Trade and investment are vital drivers of economic growth for all countries in the region. Indonesia’s strategic location makes it a key player in regional trade networks.
-
Security concerns: Shared threats such as terrorism, piracy, and transnational crime require regional cooperation. Indonesia works with its neighbours to maintain maritime security and combat these challenges.
-
Environmental challenges: Climate change, deforestation, and pollution are issues that transcend national boundaries. Indonesia collaborates with its neighbours to address these challenges and promote sustainable development.
-
Cultural exchange: Indonesia’s rich cultural heritage is influenced by its neighbours, and vice versa. Cultural exchange promotes understanding and strengthens ties between nations.
FAQs:
-
Q: What is the significance of Indonesia’s maritime borders?
-
A: Indonesia’s maritime borders are crucial for its economic prosperity and national security. They provide access to vital shipping lanes, rich fishing grounds, and potential energy resources. They also play a significant role in regional security, as they are vulnerable to threats such as piracy, illegal fishing, and transnational crime.
-
Q: What are the main challenges faced by Indonesia in its relations with its neighbours?
-
A: Indonesia faces several challenges in its relations with its neighbours, including territorial disputes, border security, and economic inequality. The country also faces the challenge of managing complex and sometimes competing interests within the ASEAN framework.
-
Q: How is Indonesia working to strengthen its relationships with its neighbours?
-
A: Indonesia is actively engaging with its neighbours through various initiatives, including bilateral and multilateral agreements, joint economic projects, and cultural exchange programmes. The country also plays a key role in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), which promotes regional cooperation and integration.
Tips for Understanding Indonesia’s Neighbours:
-
Study a map: A detailed map of Southeast Asia is essential for understanding the geographical relationships between Indonesia and its neighbours.
-
Research individual countries: Each country has its own unique history, culture, and political system. Learning about these factors can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of regional relations.
-
Follow news and current events: Stay informed about regional developments and issues that affect Indonesia and its neighbours.
-
Engage in discussions: Participate in discussions about Southeast Asia and share your knowledge with others.
Conclusion:
Understanding the map of countries around Indonesia is crucial for comprehending the country’s strategic position in Southeast Asia. Its geographical location, bordering a diverse range of nations, has shaped its history and continues to influence its present. The relationships between Indonesia and its neighbours are multifaceted, driven by shared interests in economic prosperity, regional security, environmental protection, and cultural exchange. By fostering strong and cooperative relationships with its neighbours, Indonesia can play a vital role in promoting peace, stability, and development in the region.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview: Understanding Indonesia’s Neighbours. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!