A Geographic Portrait: Japan On The World Map
A Geographic Portrait: Japan on the World Map
Related Articles: A Geographic Portrait: Japan on the World Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Portrait: Japan on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Portrait: Japan on the World Map

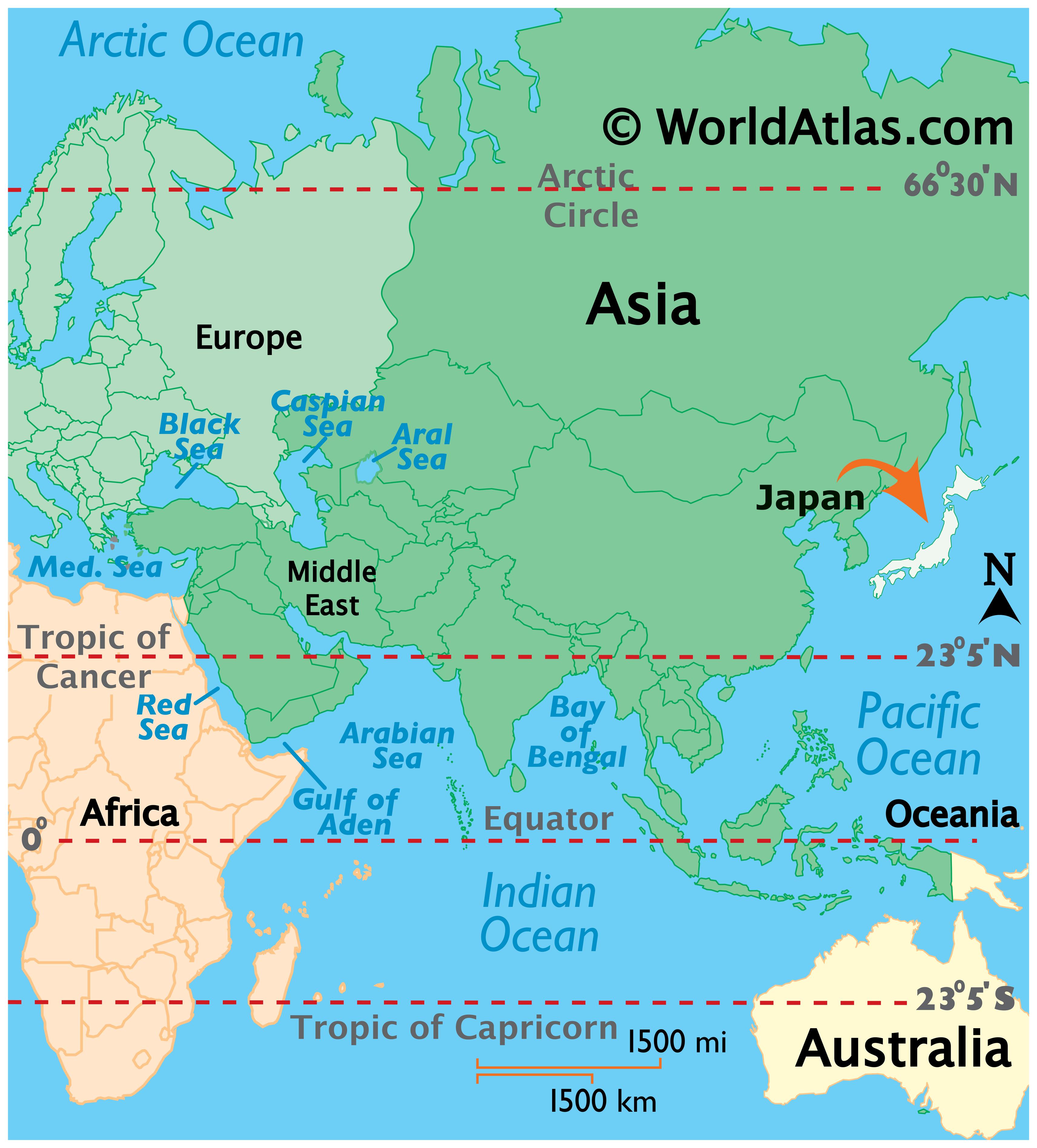
Japan, an archipelago nation in East Asia, presents a distinctive and captivating image on the world map. Its unique geographic configuration, a chain of islands stretching along the Pacific coast of the Asian mainland, offers a glimpse into the nation’s history, culture, and strategic importance.
Island Nation: A String of Jewels
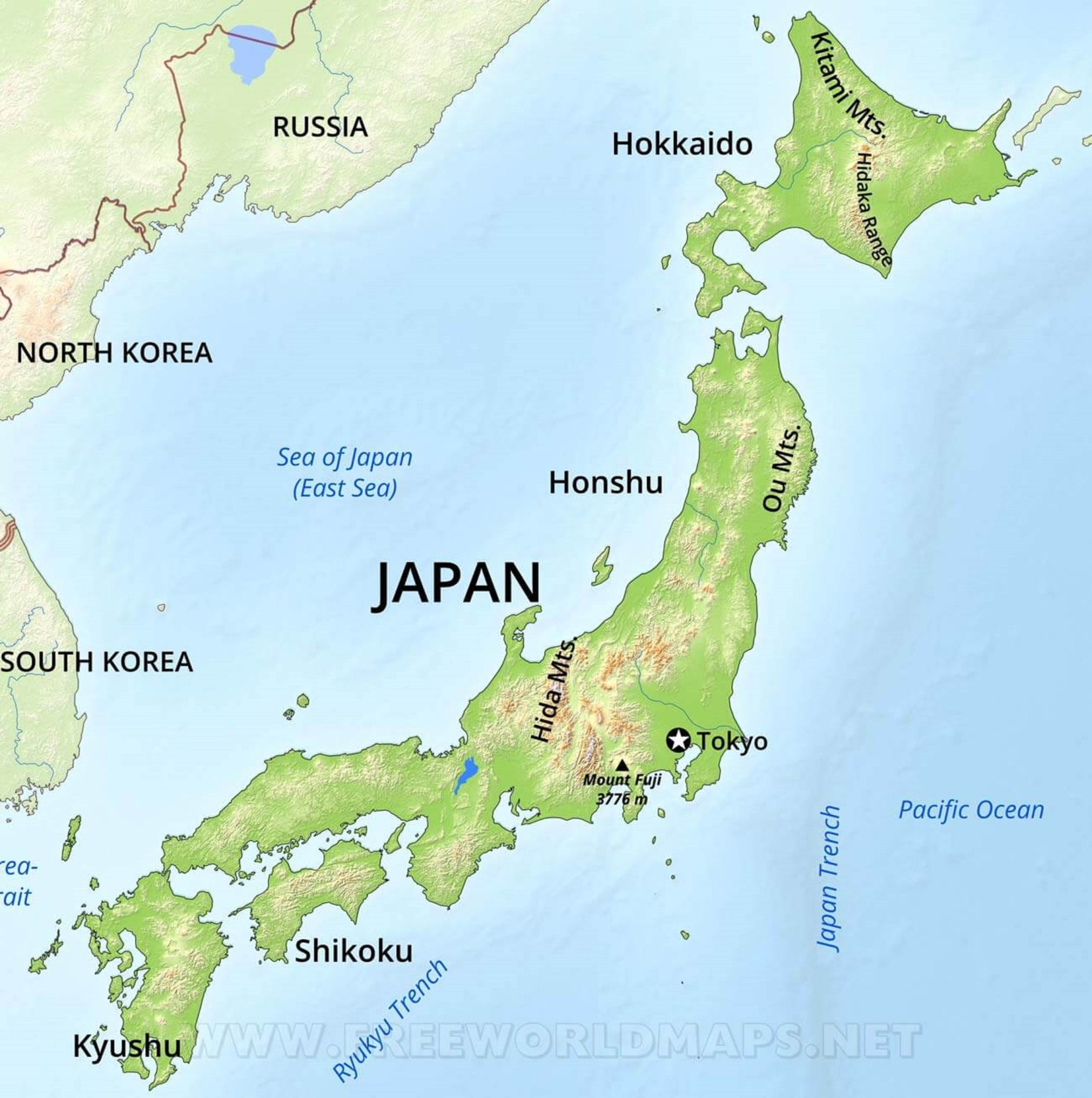
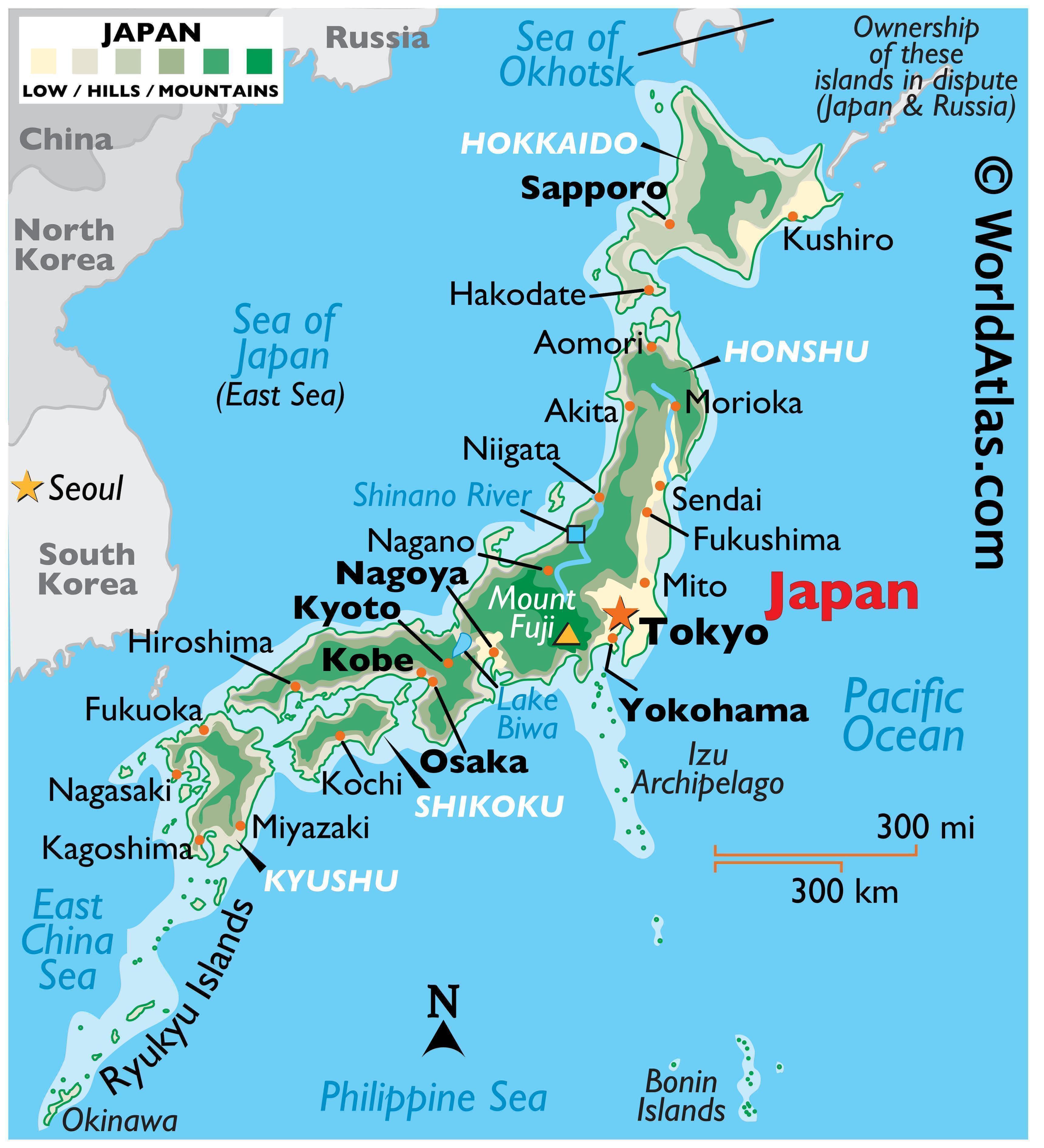
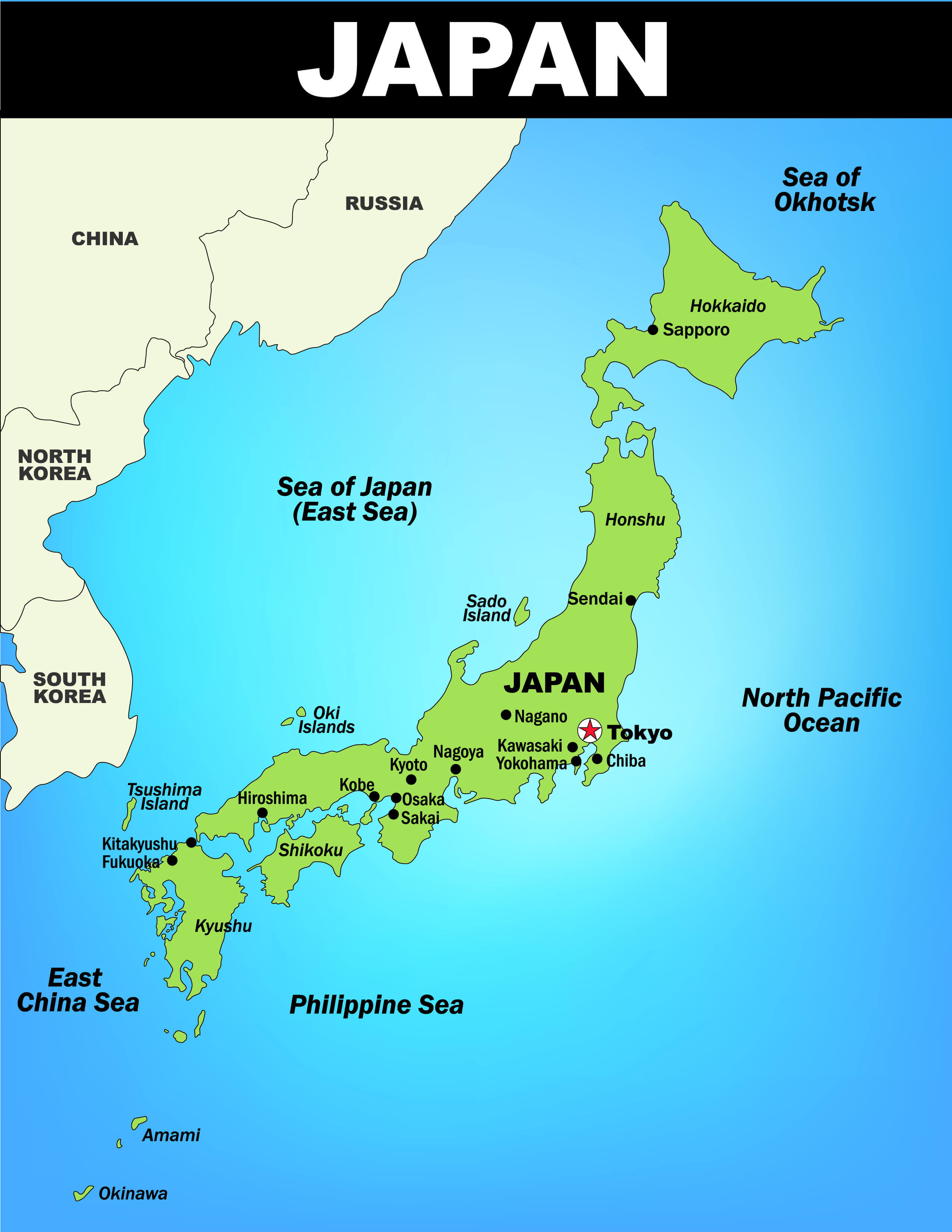
Japan’s defining characteristic is its insular nature. Comprised of four main islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and thousands of smaller islands, Japan’s geography is inherently shaped by the sea. This archipelago formation, nestled in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, has profoundly influenced the nation’s development, shaping its cultural identity and economic activities.
The Four Main Islands:
-
Hokkaido: The northernmost island, Hokkaido, is a land of rugged mountains, volcanic landscapes, and abundant natural resources. Its colder climate and vast forests support a thriving agricultural industry, particularly dairy farming and forestry.
-
Honshu: The largest and most populous island, Honshu, is home to Tokyo, the nation’s capital, and other major cities like Osaka, Kyoto, and Nagoya. Honshu’s diverse landscape encompasses towering mountains, fertile plains, and coastal regions, making it the heart of Japan’s cultural and economic activity.
-
Shikoku: The smallest of the four main islands, Shikoku is known for its lush forests, rolling hills, and serene landscapes. Its cultural heritage is rich, featuring ancient temples and pilgrimage routes.
-
Kyushu: Located in the southwest, Kyushu is a region of volcanic activity and active geothermal resources. Its diverse landscape, ranging from coastal plains to mountainous regions, has fostered a vibrant agricultural sector and a rich cultural heritage.
The Ryukyu Islands:
South of Kyushu lies the Ryukyu Islands, a chain of over 160 islands stretching towards Taiwan. These islands, with their distinct cultural heritage and subtropical climate, offer a unique glimpse into Japan’s diverse cultural tapestry.
A Land of Mountains and Volcanoes:
Japan’s geography is characterized by a mountainous terrain, with over 73% of the land covered by mountains. The Japanese Alps, a range of towering peaks in central Honshu, are a testament to the nation’s dramatic landscape. Volcanoes are a prominent feature of the Japanese landscape, with Mount Fuji, a dormant volcano, being the nation’s most iconic symbol. Volcanic activity has shaped the islands’ terrain, creating fertile soils and abundant geothermal energy resources.
Coastal Abundance:
Japan’s extensive coastline, stretching over 30,000 kilometers, plays a vital role in the nation’s economy and culture. The islands are surrounded by numerous bays, inlets, and straits, providing access to the sea and fostering a rich fishing industry. The coastline is also dotted with numerous ports and harbors, connecting Japan to the rest of the world.
Strategic Location:
Japan’s location in East Asia, at the crossroads of major trade routes, has made it a strategically important nation. Its proximity to mainland Asia, particularly China and Korea, has facilitated economic and cultural exchange, while its access to the Pacific Ocean has connected it to the wider world.
The Impact of Geography:
Japan’s unique geography has profoundly influenced its history, culture, and development. The mountainous terrain, volcanic activity, and limited arable land have shaped the nation’s agricultural practices and its reliance on marine resources. The islands’ isolation has fostered a distinct cultural identity, characterized by a strong sense of community and a deep respect for nature.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Japan’s geography offers numerous opportunities, it also presents challenges. The mountainous terrain limits arable land, while the frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions pose risks to infrastructure and human life. However, Japan’s resourcefulness and technological prowess have enabled it to overcome these challenges, developing innovative solutions for sustainable development and disaster mitigation.
FAQs:
Q: What are the main islands of Japan?
A: The four main islands of Japan are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu.
Q: What is the largest island of Japan?
A: Honshu is the largest and most populous island of Japan.
Q: What is the most famous mountain in Japan?
A: Mount Fuji, a dormant volcano, is the most iconic mountain in Japan.
Q: How does Japan’s geography influence its culture?
A: Japan’s insular nature, mountainous terrain, and limited arable land have fostered a distinct cultural identity, characterized by a strong sense of community, a deep respect for nature, and a focus on resourcefulness.
Q: What are the main economic activities in Japan?
A: Japan’s economy is driven by a diverse range of industries, including manufacturing, technology, services, and tourism. The nation is a global leader in automotive production, electronics, and robotics.
Tips:
-
Study a map of Japan: Familiarize yourself with the location and names of the main islands, major cities, and geographical features.
-
Explore the diverse landscapes: From the snow-capped peaks of Hokkaido to the subtropical beaches of Okinawa, Japan offers a wide range of landscapes to explore.
-
Learn about Japanese history and culture: Understanding the nation’s history and cultural heritage will enrich your experience.
-
Respect local customs and traditions: Japan has a strong sense of etiquette and customs. Show respect by following local norms and traditions.
Conclusion:
Japan’s geography is a defining element of its identity, shaping its history, culture, and economic development. The archipelago nation, with its diverse landscapes, strategic location, and unique cultural heritage, presents a captivating image on the world map. Understanding Japan’s geographic features is essential for appreciating the nation’s complex and fascinating history, culture, and contemporary challenges.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Portrait: Japan on the World Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!