A Geographical Overview Of Israel And Its Surrounding Area
A Geographical Overview of Israel and its Surrounding Area
Related Articles: A Geographical Overview of Israel and its Surrounding Area
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Overview of Israel and its Surrounding Area. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Overview of Israel and its Surrounding Area

The landmass encompassing Israel and its surrounding area holds profound historical, cultural, and geopolitical significance. Its intricate geography, marked by diverse landscapes and shared borders, has shaped the region’s history and continues to influence its present and future. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of this region, highlighting its key geographical features, historical context, and current political dynamics.
The Land: A Mosaic of Landscapes
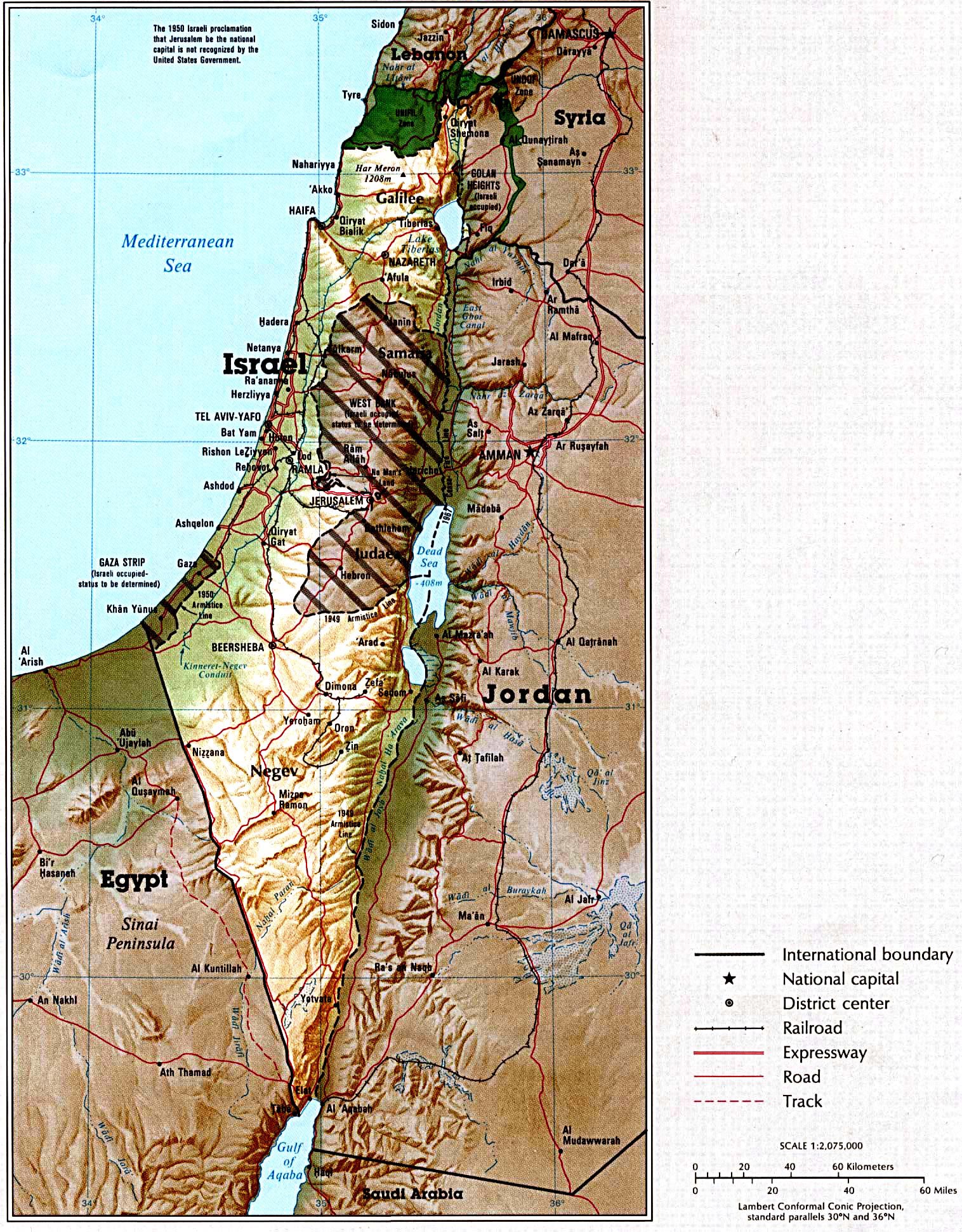
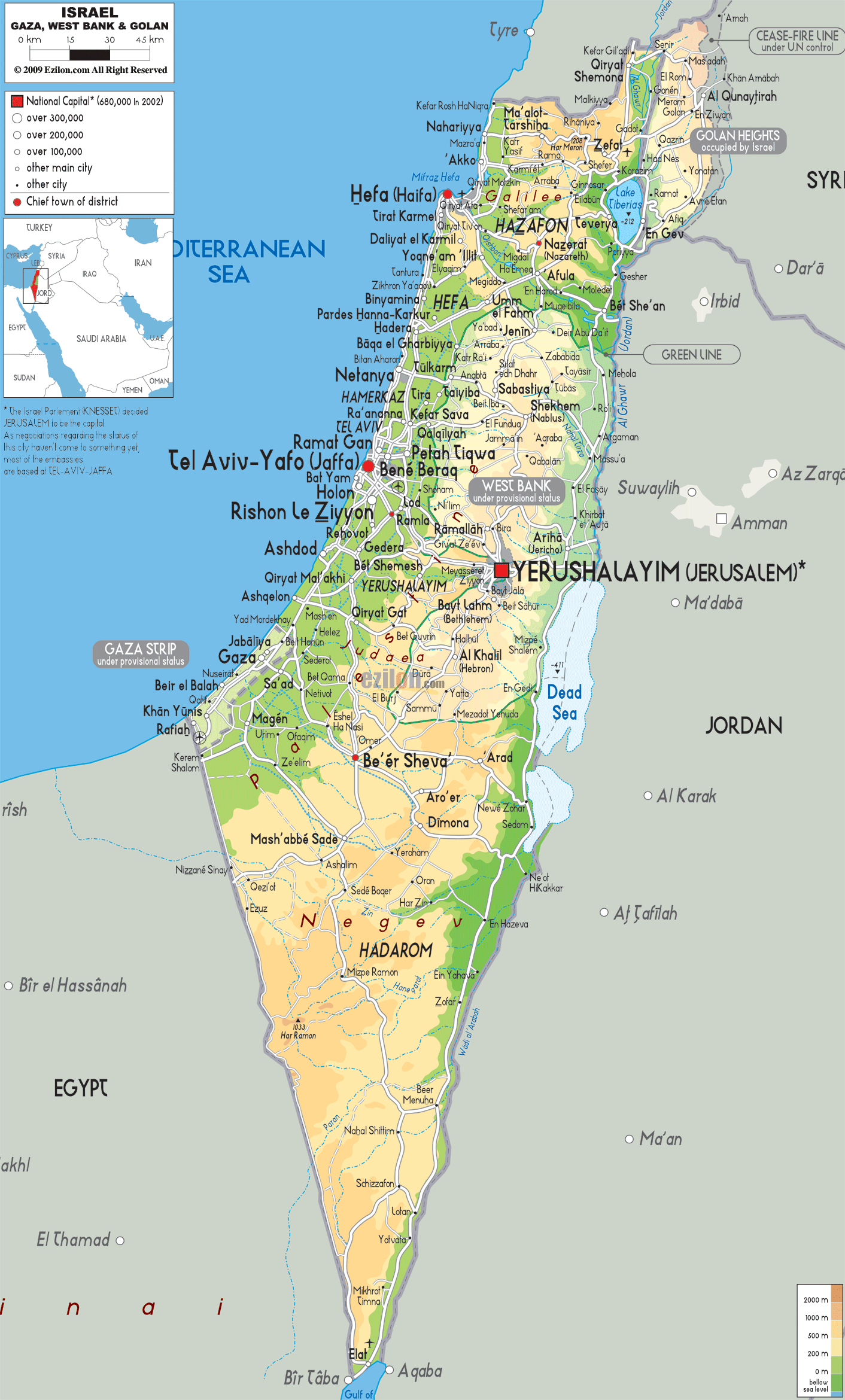
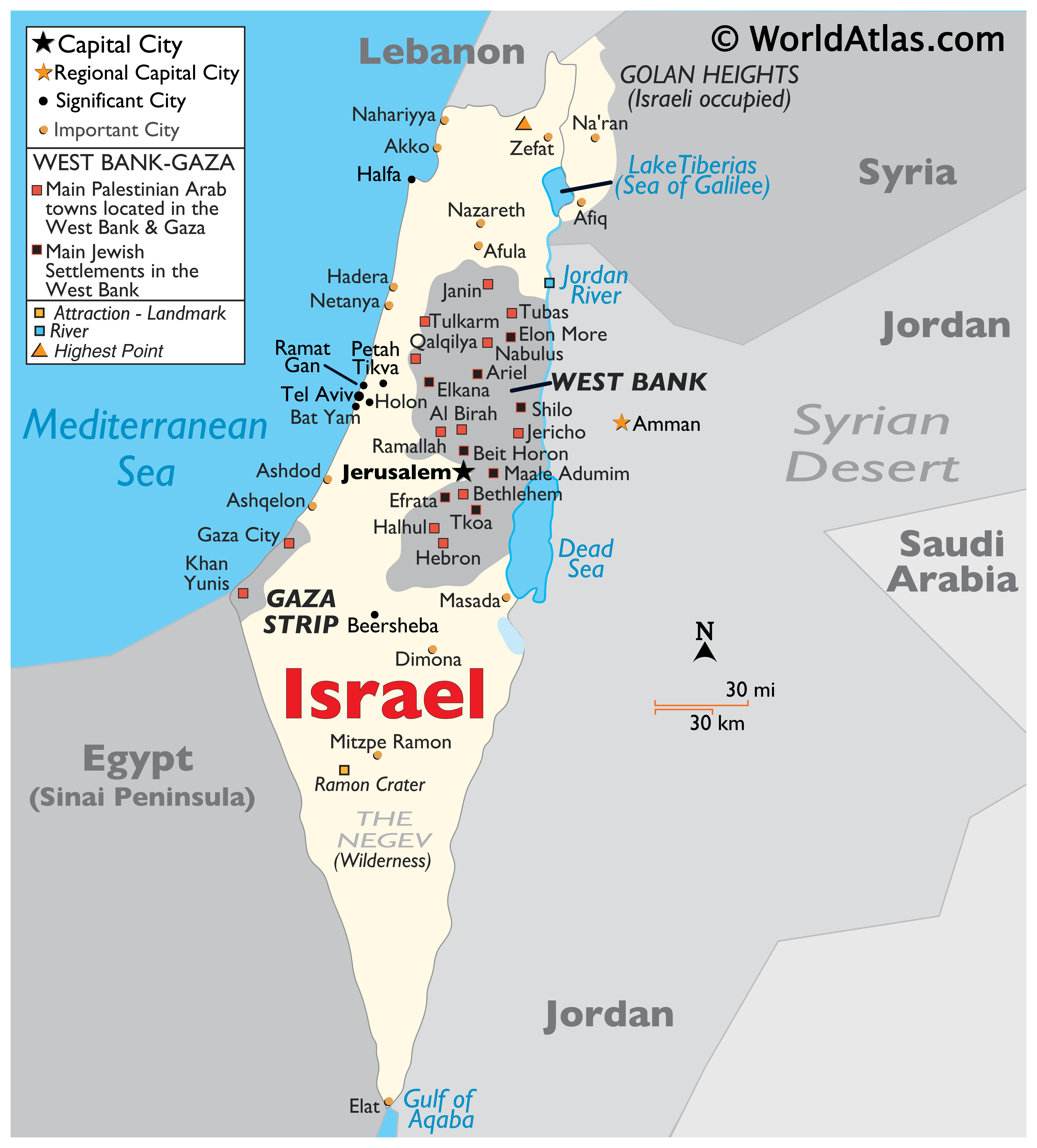
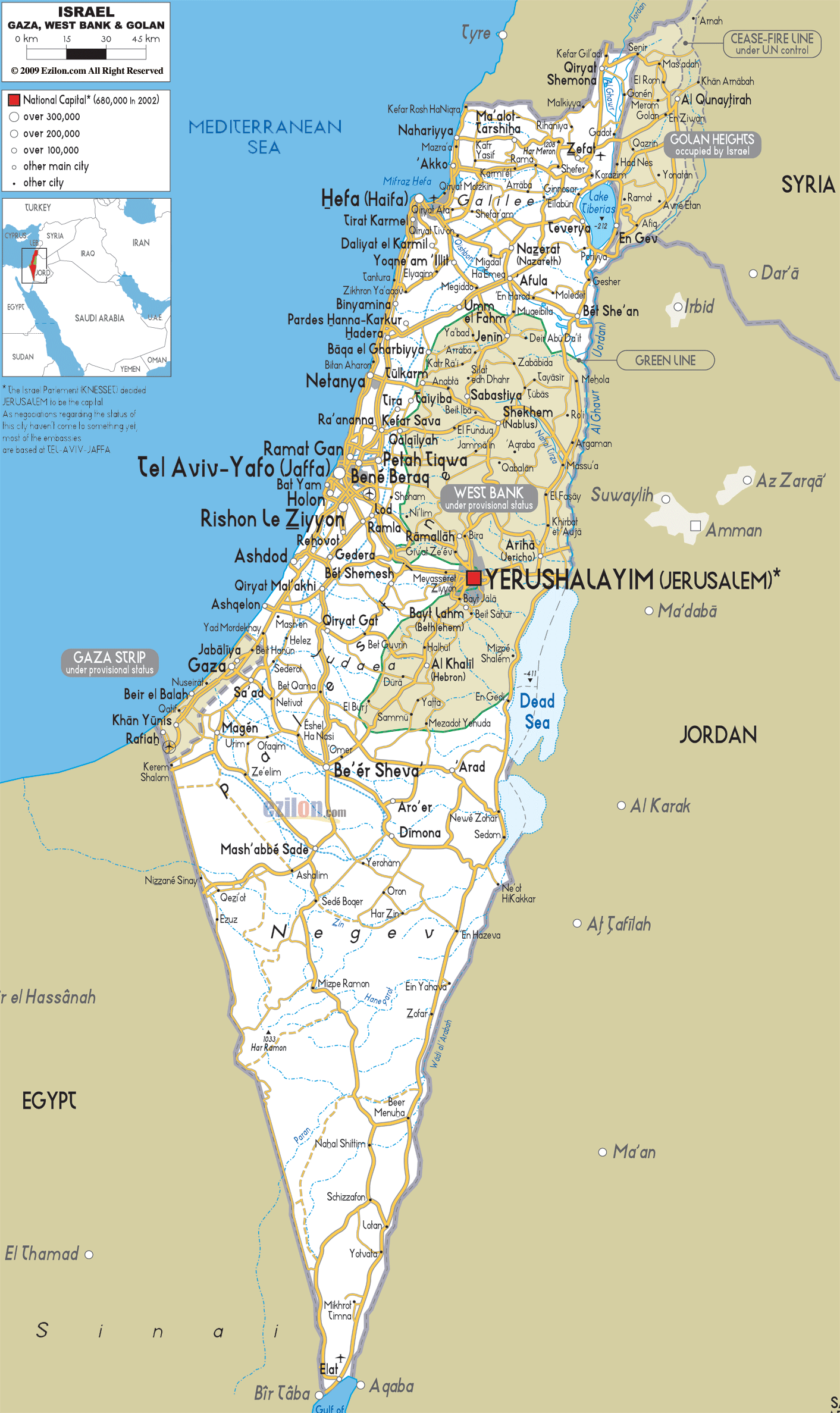
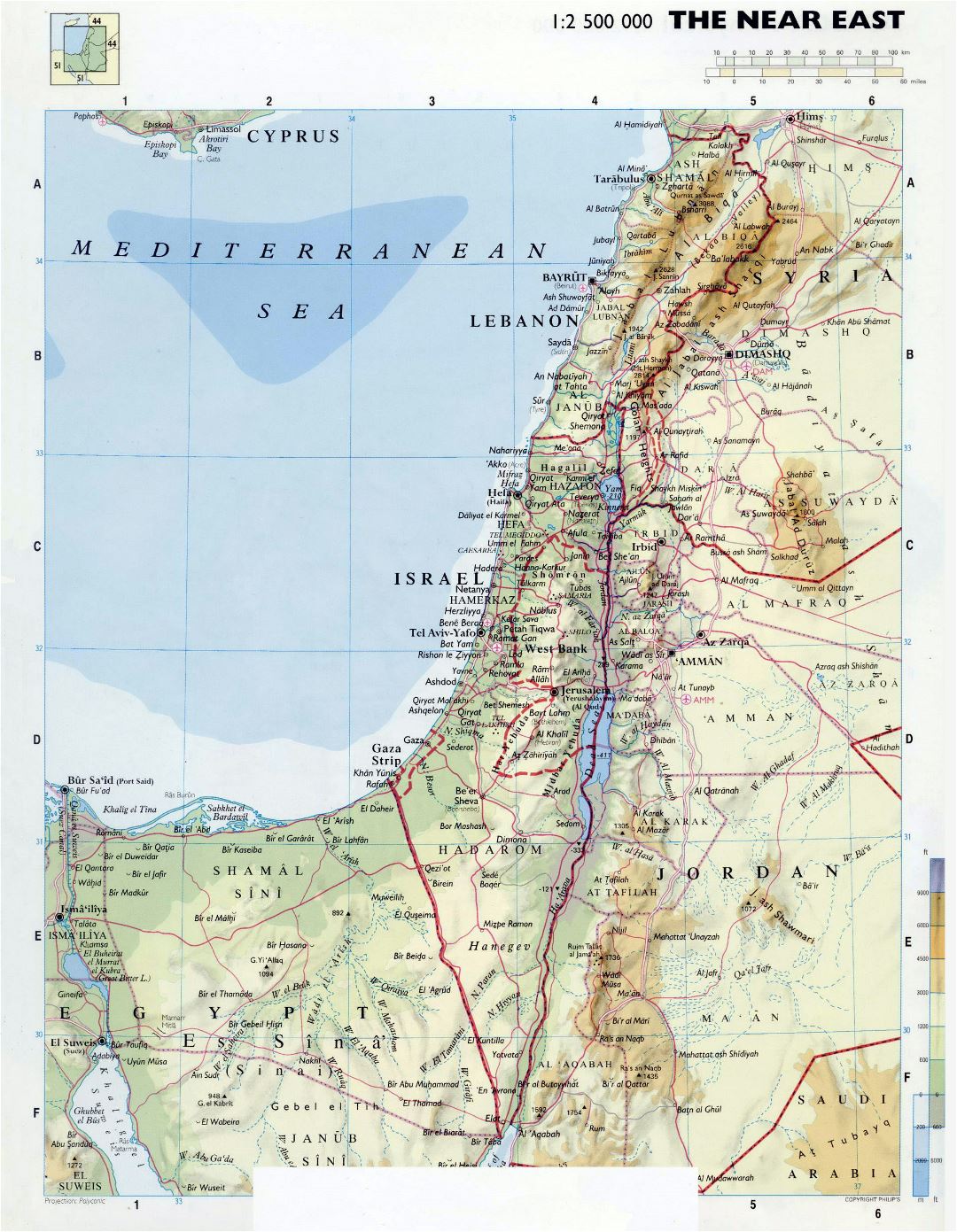
Israel’s geography is remarkably diverse, encompassing a range of landscapes within a relatively small area. The country is bordered to the west by the Mediterranean Sea, to the east by Jordan, to the north by Lebanon and Syria, and to the south by Egypt. This strategic location has contributed to its historical significance and its complex geopolitical reality.
The Coastal Plain: A narrow strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea, this region is characterized by fertile soil and a mild climate, making it ideal for agriculture. It is home to major cities like Tel Aviv and Haifa, and is a vital economic hub.
The Central Highlands: A plateau rising inland from the coastal plain, this region is characterized by rolling hills and valleys. It is home to Jerusalem, the country’s capital, and other major cities like Beit She’an and Hebron. This area is also marked by significant archaeological sites, offering insights into the region’s rich history.
The Jordan Valley: A rift valley running along the eastern border of Israel, the Jordan Valley is the lowest point on Earth outside of the Dead Sea. It is a fertile region, with a hot and dry climate, and is home to the Dead Sea, known for its high salt content and unique mineral composition.
The Negev Desert: Covering the southern portion of Israel, the Negev Desert is a vast and arid region. While sparsely populated, it holds significant mineral resources and is home to unique desert ecosystems and diverse wildlife.
The Golan Heights: A plateau overlooking the Jordan Valley, the Golan Heights is a strategically important region. It was captured by Israel from Syria during the Six-Day War in 1967 and remains a point of contention between the two countries.
The West Bank: A hilly region located between Israel and Jordan, the West Bank is home to numerous Palestinian cities and villages. Its status remains a major point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, with both sides claiming sovereignty over the territory.
The Gaza Strip: A coastal region bordering Egypt, the Gaza Strip is densely populated and governed by Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist group. It has been under Israeli blockade since 2007, resulting in ongoing humanitarian challenges.
Historical Context: A Crossroads of Civilizations
The land encompassing Israel and its surrounding area has been a crossroads of civilizations for millennia. Its strategic location, connecting Africa, Asia, and Europe, has resulted in a complex history marked by empires, conquests, and cultural exchanges.
Ancient Times: From the rise of the Canaanite civilization to the establishment of the Kingdom of Israel and the subsequent Roman conquest, the region witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires. This period saw the development of major religious traditions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, all of which hold deep significance for the region’s cultural and religious landscape.
The Ottoman Empire: From the 16th century until the early 20th century, the region was part of the Ottoman Empire. This period saw relative stability and the development of trade routes and economic activity. However, it also witnessed the rise of nationalist movements, setting the stage for the region’s transformation in the 20th century.
The British Mandate: Following World War I, the region was placed under British rule as the British Mandate for Palestine. This period witnessed increasing tensions between Jewish and Arab populations, culminating in the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948.
The State of Israel: The establishment of Israel in 1948 led to the Arab-Israeli War, resulting in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians and the ongoing conflict between Israel and its Arab neighbors. The subsequent decades saw multiple wars and peace negotiations, with the region remaining a focal point of international attention.
Current Political Dynamics: A Complex Landscape
The region encompassing Israel and its surrounding area remains a complex and volatile geopolitical landscape. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict continues to dominate the region’s political discourse, with ongoing negotiations and a lack of a lasting peace agreement.
The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The core issue of the conflict revolves around the status of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, with both sides claiming sovereignty over the territory. The conflict has led to a protracted cycle of violence and instability, affecting the lives of millions of people.
Regional Dynamics: The region is also marked by complex relationships between Israel and its Arab neighbors. While peace agreements have been signed with Egypt and Jordan, tensions persist with Syria and Lebanon. The rise of Islamic extremism in the region, particularly in the form of ISIS and other groups, has further complicated the geopolitical landscape.
International Involvement: The region has been a focus of international attention for decades. The United Nations plays a significant role in mediating peace negotiations and providing humanitarian assistance. The United States, as a major ally of Israel, has been deeply involved in the region’s affairs.
Challenges and Prospects: The region faces numerous challenges, including economic inequality, environmental degradation, and the ongoing threat of terrorism. However, there are also opportunities for progress, particularly in the areas of economic cooperation and regional integration.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea is a hypersaline lake, known for its high salt content and unique mineral composition. It is the lowest point on Earth outside of the Dead Sea, and its mineral-rich waters have been used for therapeutic purposes for centuries.
2. What is the current status of the West Bank?
The status of the West Bank remains a major point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Both Israel and Palestine claim sovereignty over the territory, with Israel maintaining control over most of the land.
3. What are the main challenges facing the region?
The region faces numerous challenges, including the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, economic inequality, environmental degradation, and the ongoing threat of terrorism.
4. What are the prospects for peace in the region?
The prospects for peace in the region remain uncertain. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains a major obstacle to regional stability, and the rise of Islamic extremism has further complicated the geopolitical landscape.
5. What role does the international community play in the region?
The international community plays a significant role in the region, particularly through the United Nations, which mediates peace negotiations and provides humanitarian assistance. The United States, as a major ally of Israel, has also been deeply involved in the region’s affairs.
Tips
1. Understand the historical context: To gain a deeper understanding of the region’s current dynamics, it is crucial to study its rich and complex history.
2. Explore diverse perspectives: Seek out information from a variety of sources, including those from both Israeli and Palestinian perspectives.
3. Follow current events: Stay informed about the latest developments in the region through reliable news sources.
4. Engage in respectful dialogue: When discussing the region’s issues, it is essential to engage in respectful dialogue, acknowledging the complexity of the situation and the diverse perspectives involved.
Conclusion
The landmass encompassing Israel and its surrounding area is a complex and dynamic region, marked by diverse landscapes, rich history, and ongoing political challenges. Understanding the region’s geography, historical context, and current political dynamics is crucial for appreciating its significance and the complexities of its present and future. The region’s future remains uncertain, with ongoing challenges and opportunities for progress. The international community plays a vital role in promoting peace and stability in the region, while recognizing the importance of addressing the underlying issues and promoting dialogue and understanding between all parties involved.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Overview of Israel and its Surrounding Area. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!