Navigating The Archipelago: A Comprehensive Exploration Of Japan’s Geography
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Exploration of Japan’s Geography
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Exploration of Japan’s Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Exploration of Japan’s Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Exploration of Japan’s Geography
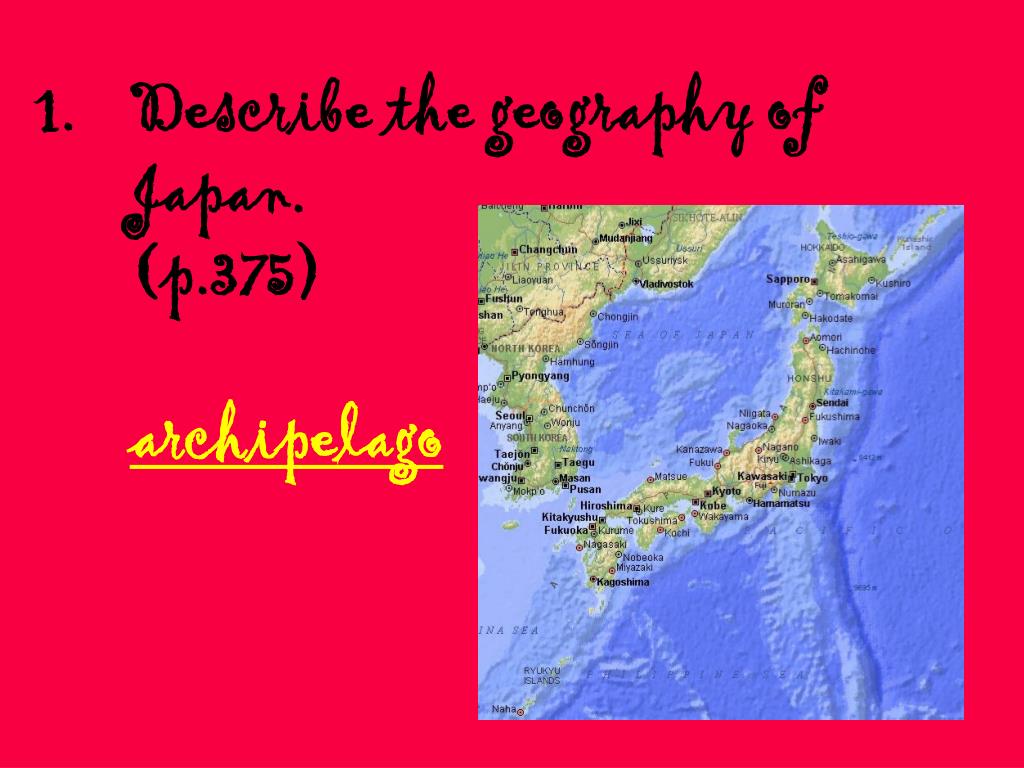
Japan, an island nation nestled in the northwest Pacific Ocean, is a land of contrasts. From the towering peaks of the Japanese Alps to the bustling megacities of Tokyo and Osaka, the archipelago presents a diverse and captivating landscape. Understanding its geographical features is crucial for appreciating its unique history, culture, and contemporary society.
A Land Shaped by Tectonic Forces:
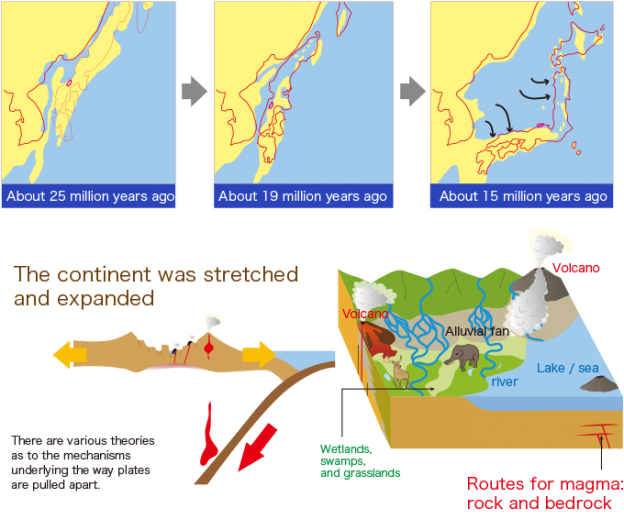
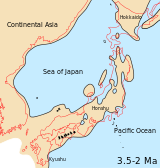
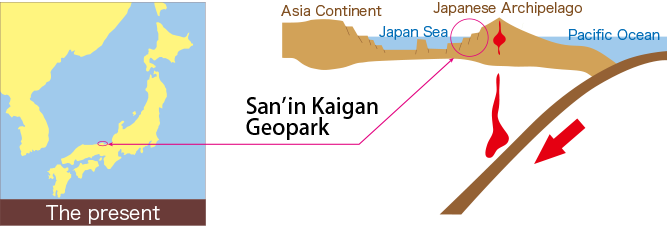
Japan’s geography is a product of complex geological processes. The archipelago is located at the convergence of four tectonic plates: the Eurasian, North American, Philippine Sea, and Pacific plates. This intense tectonic activity has shaped the country’s dramatic landscape, characterized by:
- Volcanoes: Japan is home to over 100 active volcanoes, including Mount Fuji, the country’s highest peak. These volcanic mountains have played a significant role in shaping the nation’s landscape and culture, providing fertile soils for agriculture and serving as spiritual symbols.
- Earthquakes: Situated on the Pacific Ring of Fire, Japan experiences frequent earthquakes, some of which have been devastating. The country has a long history of adapting to seismic activity, developing sophisticated earthquake-resistant infrastructure and disaster preparedness protocols.
- Mountains: Japan is a mountainous country, with over 73% of its land area covered by mountains. These mountain ranges, including the Japanese Alps and the Chubu Mountains, have traditionally served as barriers between regions, influencing cultural development and transportation patterns.
- Coastline: With a coastline stretching over 33,000 kilometers, Japan is an island nation with numerous bays, inlets, and peninsulas. This extensive coastline has fostered a strong maritime culture, influencing fishing, trade, and transportation.
Regional Diversity and Cultural Tapestry:
Japan’s diverse geography has given rise to distinct regional cultures and traditions. The country can be broadly divided into four main regions:
- Hokkaido: The northernmost island, Hokkaido is known for its vast forests, volcanic landscapes, and cool climate. It is a popular destination for outdoor activities like skiing, hiking, and fishing.
- Honshu: The largest island, Honshu is home to Tokyo, Osaka, and other major cities. It is a densely populated region with a vibrant cultural scene, diverse industries, and modern infrastructure.
- Shikoku: The smallest of the four main islands, Shikoku is known for its lush forests, scenic mountains, and Buddhist temples. It is a region rich in history and spirituality, offering a tranquil escape from the hustle and bustle of urban life.
- Kyushu: The southernmost island, Kyushu is characterized by its volcanic landscapes, hot springs, and subtropical climate. It is a region known for its vibrant culture, traditional crafts, and delicious cuisine.
Navigating the Archipelago: Transportation and Infrastructure:
Japan’s geographical features have influenced its transportation infrastructure. The country has a well-developed network of:
- High-speed railways (Shinkansen): The Shinkansen, also known as the "bullet train," is a high-speed rail system that connects major cities across the country. It is renowned for its punctuality, efficiency, and comfort.
- Roads: Japan has a vast network of highways and roads, connecting cities and towns across the archipelago. The country’s road infrastructure is known for its quality and safety.
- Airports: With numerous international airports, Japan is well-connected to the rest of the world. The country’s airports are known for their efficiency and modern facilities.
- Seaports: Japan’s extensive coastline has fostered a strong maritime culture, with numerous seaports serving as major hubs for trade and transportation.
Environmental Challenges and Sustainability:
Japan’s geography also presents challenges in terms of environmental sustainability:
- Natural Disasters: The country’s vulnerability to earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions necessitates robust disaster preparedness and mitigation measures.
- Deforestation: Japan’s mountainous terrain and rapid urbanization have led to significant deforestation, impacting biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Pollution: Industrialization and urbanization have contributed to air and water pollution in some areas, posing challenges for public health and environmental protection.
Importance of Geographical Understanding:
Understanding Japan’s geography is crucial for appreciating its history, culture, and contemporary society. It helps explain:
- Cultural Diversity: The archipelago’s diverse landscapes and regional differences have shaped unique cultural traditions, languages, and cuisines.
- Historical Development: The country’s geographical features have influenced its historical development, from the rise of feudal lords to the emergence of modern cities.
- Economic Growth: Japan’s location and resources have played a significant role in its economic development, fostering trade and industrialization.
- Environmental Challenges: Understanding the country’s geographical vulnerabilities and environmental challenges is essential for developing sustainable solutions.
FAQs by Map Japan Area:
Q: What is the highest mountain in Japan?
A: Mount Fuji, a stratovolcano located on Honshu island, is the highest mountain in Japan, standing at 3,776 meters (12,388 feet).
Q: What is the largest city in Japan?
A: Tokyo, located on Honshu island, is the largest city in Japan with a population of over 13.6 million.
Q: How many islands are there in Japan?
A: Japan is an archipelago consisting of over 6,800 islands, but only about 430 are inhabited.
Q: What is the capital city of Japan?
A: Tokyo is the capital city of Japan, serving as the country’s political, economic, and cultural center.
Q: What is the most popular tourist destination in Japan?
A: Tokyo, with its iconic landmarks like the Tokyo Skytree, the Imperial Palace, and the bustling Shibuya crossing, is a popular tourist destination. Other popular destinations include Kyoto, Osaka, and Mount Fuji.
Tips by Map Japan Area:
- Travel by Shinkansen: Experience the efficiency and comfort of Japan’s high-speed rail system.
- Explore regional cultures: Visit different regions to experience the diverse cultural traditions and cuisines of Japan.
- Respect Japanese customs: Learn about Japanese etiquette and customs to ensure a pleasant and respectful experience.
- Prepare for earthquakes: Familiarize yourself with earthquake safety procedures and be aware of potential risks.
- Embrace the outdoors: Explore Japan’s stunning natural landscapes, from the volcanic mountains to the serene coastal areas.
Conclusion by Map Japan Area:
Japan’s geography is a complex and fascinating tapestry, shaped by tectonic forces and characterized by regional diversity. From its towering mountains to its bustling cities, the archipelago offers a unique blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and modern innovation. Understanding the country’s geography is essential for appreciating its history, culture, and contemporary society, fostering a deeper understanding of this island nation and its remarkable people.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Exploration of Japan’s Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!