Navigating The Geopolitical Landscape: A Comprehensive Look At Israel’s Neighbors
Navigating the Geopolitical Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Israel’s Neighbors
Related Articles: Navigating the Geopolitical Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Israel’s Neighbors
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Geopolitical Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Israel’s Neighbors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Geopolitical Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Israel’s Neighbors

The Middle East, a region known for its complex history and diverse cultures, is home to Israel, a nation that has endured a turbulent journey marked by conflict and diplomacy. Understanding the geographic context of Israel, particularly its neighboring countries, is crucial for comprehending the intricate dynamics of the region. This article delves into the geopolitical landscape surrounding Israel, providing a detailed analysis of its neighboring states and the historical, cultural, and political factors that shape their relationships.
A Mosaic of Nations: Israel’s Neighbors
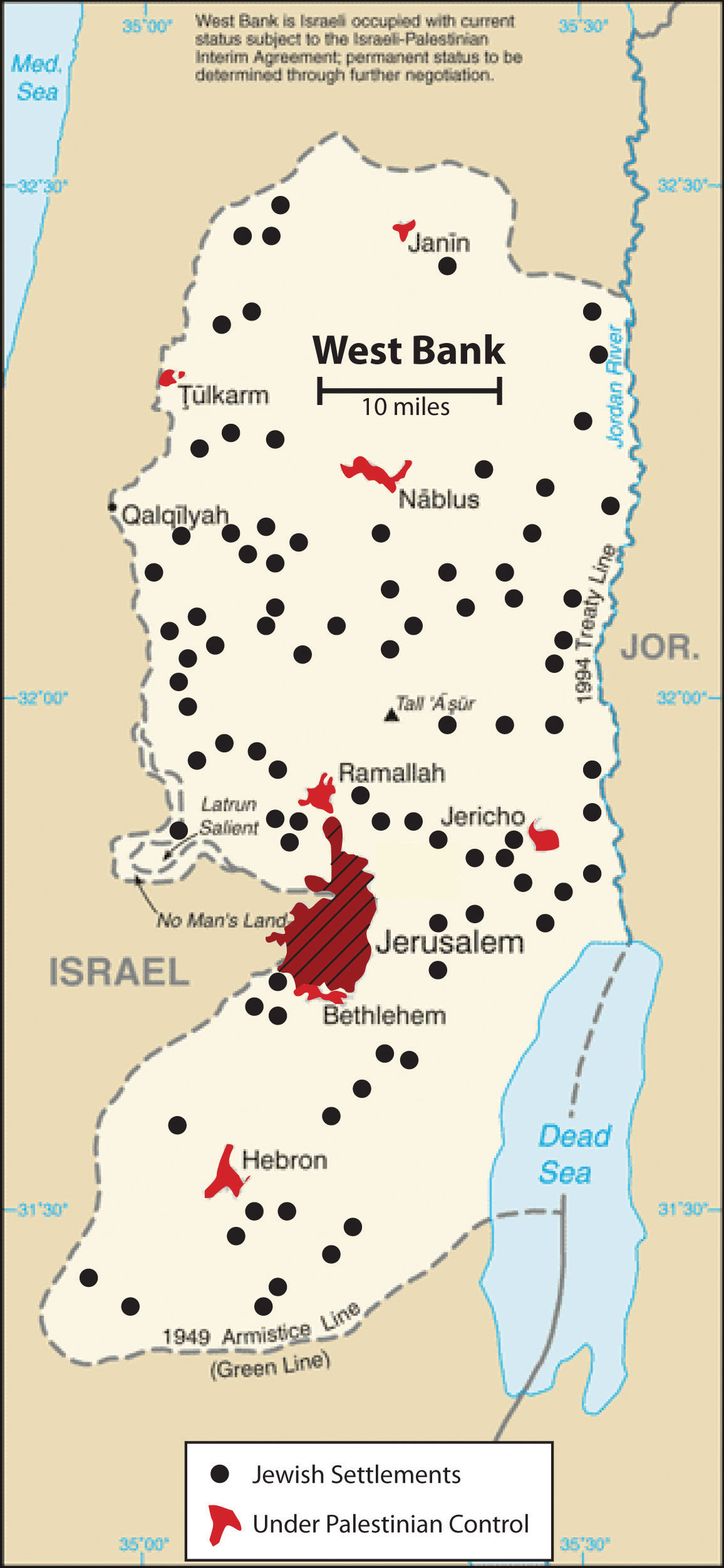
Israel’s immediate neighbors are a diverse collection of nations, each with its unique history, culture, and political system. These neighbors, depicted on a map, provide a visual representation of the intricate web of relationships that define the region:
- Lebanon: Situated to the north of Israel, Lebanon shares a long and complex history with its southern neighbor. The two nations have engaged in numerous conflicts, most notably the 2006 Lebanon War, fueled by territorial disputes and the presence of Hezbollah, a powerful Lebanese Shia militia.
- Syria: Sharing a border to the northeast, Syria has historically been a major player in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The two countries have been engaged in a long-standing conflict, marked by the 1967 Six-Day War and the 1973 Yom Kippur War. The ongoing Syrian Civil War has further complicated the relationship.
- Jordan: To the east of Israel, Jordan maintains a relatively stable relationship with its neighbor. The two countries signed a peace treaty in 1994, fostering cooperation in areas such as water management and trade. However, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict continues to cast a shadow on their relationship.
- Egypt: Situated to the southwest of Israel, Egypt was a long-time adversary but has become a crucial strategic partner. The two countries signed a peace treaty in 1979, a landmark agreement that has significantly reduced tensions in the region.
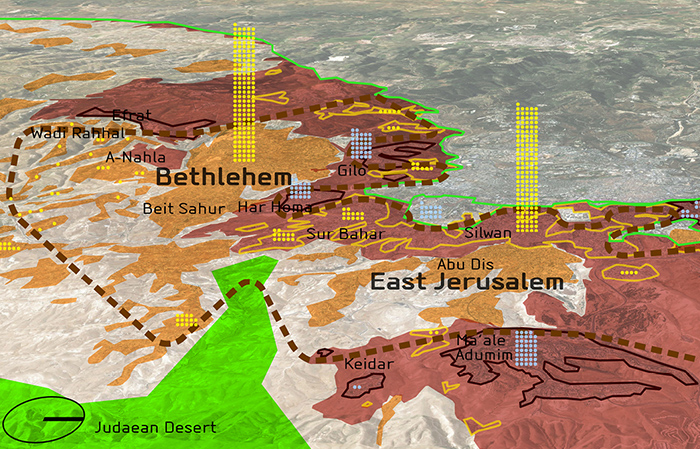
- The Gaza Strip and the West Bank: These Palestinian territories, located along the Mediterranean coast and in the West Bank, respectively, are at the heart of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The ongoing struggle for Palestinian statehood and the control of these territories remain a major source of tension.
Understanding the Dynamics: Historical and Political Factors
The relationships between Israel and its neighbors are shaped by a confluence of historical, cultural, and political factors. A deeper understanding of these factors reveals the complexities of the region:
- Historical Conflicts: The region’s history is marred by numerous conflicts, including the Arab-Israeli wars, the Palestinian-Israeli conflict, and the ongoing Syrian Civil War. These conflicts have left lasting scars, creating deep-seated mistrust and animosity between the involved parties.
- Religious and Cultural Differences: The region is home to a diverse array of religious and cultural groups, including Jews, Muslims, Christians, and Druze. These differences have often fueled tensions and conflicts, particularly between Israel and its Arab neighbors.
- Territorial Disputes: Disputes over land and resources, particularly in the West Bank and the Golan Heights, have been a major source of conflict. The ongoing negotiations for a two-state solution between Israel and the Palestinians remain fraught with challenges.
- Political Ideologies: The political ideologies of Israel and its neighbors, ranging from secularism to religious fundamentalism, have also played a role in shaping their relationships. The rise of Islamist movements in the region has further complicated the dynamics.
- International Influence: External powers, including the United States, Russia, and the European Union, have significant influence in the region. Their policies and interventions have often impacted the relationships between Israel and its neighbors.
Beyond the Conflict: Areas of Cooperation
Despite the challenges and conflicts, there are also areas of cooperation between Israel and its neighbors. These areas offer a glimmer of hope for a more peaceful future:
- Economic Cooperation: Israel has engaged in economic cooperation with some of its neighbors, particularly Jordan and Egypt. This cooperation has focused on trade, tourism, and infrastructure development.
- Water Management: Water scarcity is a major challenge in the region. Israel has been involved in collaborative projects with its neighbors to address this issue, particularly in the Jordan River basin.
- Security Cooperation: In certain cases, Israel has engaged in security cooperation with its neighbors, particularly with Jordan, to combat terrorism and address regional security concerns.
- Cultural Exchange: Cultural exchanges between Israel and its neighbors have fostered dialogue and understanding. These exchanges have focused on music, art, and education.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. Why is the relationship between Israel and its neighbors so complex?
The relationship between Israel and its neighbors is complex due to a combination of historical conflicts, religious and cultural differences, territorial disputes, political ideologies, and international influence.
2. What are the main challenges to peace in the region?
The main challenges to peace in the region include the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the ongoing Syrian Civil War, and the rise of Islamist movements.
3. Are there any signs of hope for a more peaceful future?
While the challenges are significant, there are signs of hope for a more peaceful future, including economic cooperation, water management initiatives, and cultural exchanges.
4. What role does the international community play in the region?
The international community plays a significant role in the region, through diplomatic efforts, economic aid, and military interventions. However, its influence is often limited by the complex dynamics and competing interests of the involved parties.
Tips for Navigating the Geopolitical Landscape
- Stay informed: Keep up with current events and developments in the region through reliable news sources.
- Seek diverse perspectives: Explore a range of viewpoints and avoid relying on biased or one-sided information.
- Understand the historical context: Gain a comprehensive understanding of the region’s history, including the roots of conflicts and the evolution of relationships.
- Engage in constructive dialogue: Participate in respectful discussions about the region, avoiding generalizations and stereotypes.
- Support peace-building efforts: Advocate for initiatives that promote dialogue, reconciliation, and cooperation.
Conclusion: A Complex and Evolving Landscape
The map of countries near Israel reveals a complex and dynamic geopolitical landscape. Understanding the historical, cultural, and political factors that shape the relationships between Israel and its neighbors is essential for navigating this intricate region. While challenges abound, the potential for cooperation and peace remains. By engaging in informed dialogue, promoting understanding, and supporting peace-building efforts, we can contribute to a more stable and prosperous future for the Middle East.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Geopolitical Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Israel’s Neighbors. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!