Navigating The Landscape: A Deep Dive Into The Put Method In Java Maps
Navigating the Landscape: A Deep Dive into the put Method in Java Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Deep Dive into the put Method in Java Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: A Deep Dive into the put Method in Java Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: A Deep Dive into the put Method in Java Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape: A Deep Dive into the put Method in Java Maps
- 3.1 Unveiling the Essence of put
- 3.2 Demystifying the Return Value
- 3.3 Exploring the Variants of put
- 3.4 The Importance of Understanding put
- 3.5 FAQs: Navigating the put Method
- 3.6 Tips for Effective put Usage
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Key-Value Management
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape: A Deep Dive into the put Method in Java Maps
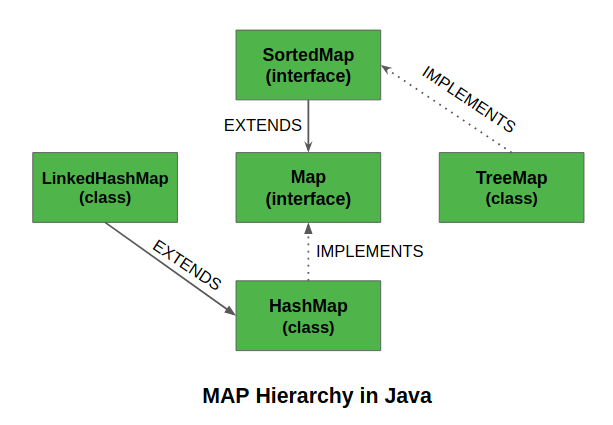
The Java Map interface, a cornerstone of data structures, provides a versatile mechanism for storing and retrieving key-value pairs. One of its most fundamental methods, put, plays a pivotal role in populating and manipulating these key-value associations. Understanding the intricacies of put is crucial for efficiently leveraging the power of maps in Java applications.
Unveiling the Essence of put
The put method, a core component of the Map interface, enables the insertion or modification of key-value pairs within a map. Its signature, typically defined as V put(K key, V value), highlights its role in associating a specific key (K) with a corresponding value (V).
Here’s a breakdown of how put functions:
- Key Lookup: The method first attempts to locate the specified key within the map.
-
Insertion: If the key is not found,
putinserts a new entry consisting of the provided key and value. -
Modification: If the key already exists,
putoverwrites the existing value associated with that key with the new value provided.
This dynamic behavior, where put seamlessly handles both insertion and modification, makes it a versatile tool for managing key-value relationships within maps.
Demystifying the Return Value
The put method in Java maps returns a value, specifically the value previously associated with the key, if the key already existed in the map. If the key was not present, put returns null. This return value provides valuable information about the outcome of the operation, enabling developers to determine whether an entry was inserted or modified.
Exploring the Variants of put
While the standard put method effectively handles basic key-value insertion and modification, the Map interface offers additional variants that cater to specific use cases:
-
putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m): This method efficiently inserts all key-value pairs from a given map (m) into the current map. -
compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction): This method allows for more complex key-value manipulation. It applies a providedremappingFunctionto the key and its existing value (if present), and updates the map based on the function’s result. -
computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction): This method inserts a new key-value pair only if the key is not already present in the map. It uses amappingFunctionto generate the value based on the key. -
computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction): This method modifies the value associated with a key only if the key already exists in the map. It uses aremappingFunctionto generate the new value based on the key and its existing value. -
merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction): This method allows for merging the existing value associated with a key with the provided value, using aremappingFunctionto determine the resulting value.
These variants empower developers to tailor the put operation to their specific needs, enabling more sophisticated map manipulation.
The Importance of Understanding put
The put method is a fundamental building block for working with Java maps. Its ability to efficiently manage key-value associations, coupled with its versatile variants, makes it a crucial tool for:
-
Data Storage and Retrieval: Maps serve as highly efficient data structures for storing and retrieving information based on unique keys. The
putmethod facilitates the population and modification of these key-value pairs. -
Caching and Lookup Optimization: Maps are often used for caching frequently accessed data, allowing for faster retrieval. The
putmethod ensures that cached data is readily available and can be efficiently updated. -
Configuration Management: Maps are ideal for storing application configurations, where keys represent settings and values hold their corresponding values. The
putmethod enables dynamic configuration updates. -
Mapping Data Transformations: Maps can be used to implement data transformations, where keys represent input values and values represent their corresponding output values. The
putmethod facilitates the mapping of input data to output data.
FAQs: Navigating the put Method
1. What happens if I try to put a key that already exists in the map?
The put method in Java maps will overwrite the existing value associated with the key with the new value provided. This behavior allows for dynamic updates to key-value pairs within the map.
2. What if I try to put a null key into a map?
The behavior of attempting to put a null key into a map depends on the specific map implementation. Some implementations may allow null keys, while others may throw an exception. It’s generally recommended to avoid using null keys to maintain code clarity and consistency.
3. How does the put method handle collisions between keys?
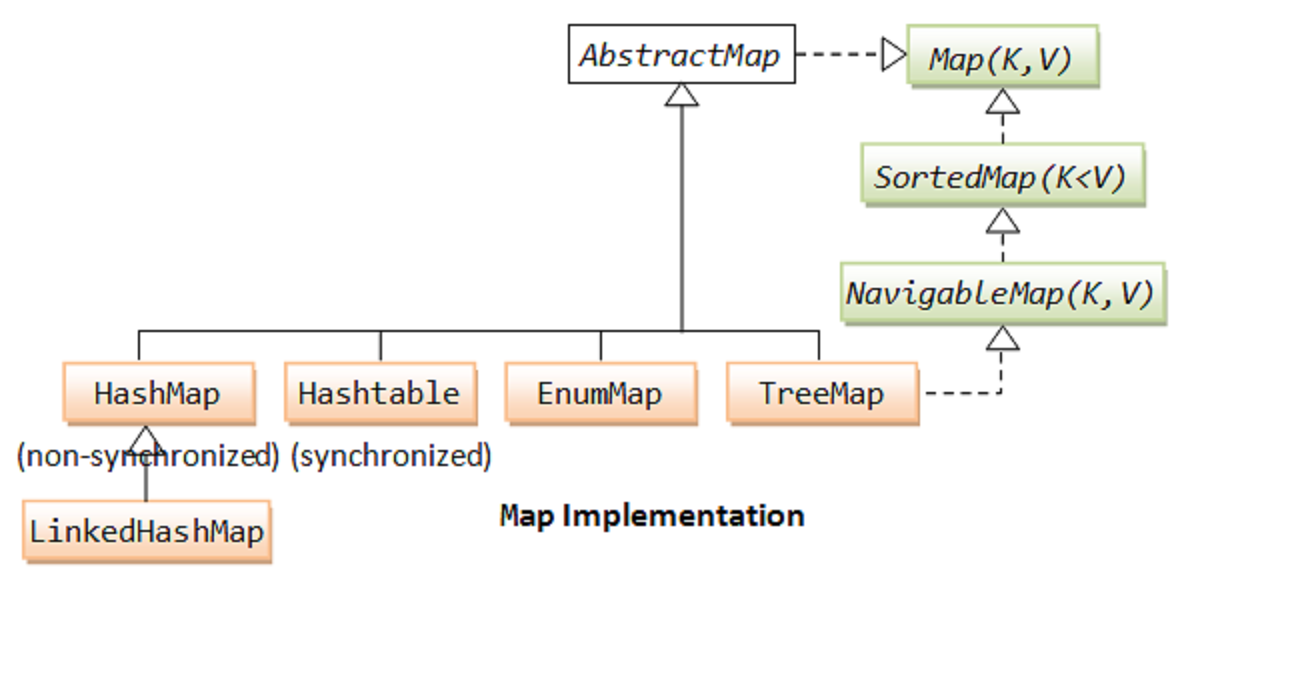
The put method does not directly handle key collisions. Instead, the underlying map implementation, such as HashMap or TreeMap, utilizes hashing algorithms and data structures to efficiently resolve collisions and ensure unique key associations.
4. What is the difference between put and putAll?
The put method inserts a single key-value pair into the map, while putAll inserts all key-value pairs from another map into the current map. putAll provides a convenient way to bulk-populate a map with data from another source.
5. How can I ensure that a key-value pair is added only if the key is not already present in the map?
The computeIfAbsent method provides a mechanism for adding a key-value pair only if the key is not already present in the map. It uses a mappingFunction to generate the value based on the key, ensuring that the value is only added if the key is truly absent.
Tips for Effective put Usage
-
Understand the Map Implementation: Different map implementations, such as
HashMap,TreeMap, andLinkedHashMap, have varying performance characteristics and data ordering behavior. Choose the implementation that best suits your application’s needs. - Avoid Null Keys: While some map implementations may allow null keys, it’s generally recommended to avoid them to maintain code clarity and consistency.
-
Consider Performance: For frequent key-value insertions,
HashMapis often a good choice due to its efficient hashing algorithm. If ordering is important,TreeMaporLinkedHashMapmay be more suitable. -
Leverage Variants: The
Mapinterface provides a range ofputvariants, includingputAll,compute,computeIfAbsent, andmerge. Choose the variant that best aligns with your specific use case for optimized map manipulation. - Document Assumptions: Clearly document any assumptions about null keys, key collisions, and data ordering behavior to ensure code maintainability and prevent unexpected behavior.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Key-Value Management
The put method in Java maps is a fundamental and versatile tool for managing key-value associations. Its ability to seamlessly handle insertion and modification, coupled with its various variants, makes it indispensable for a wide range of applications. Understanding the intricacies of put and its variations empowers developers to effectively leverage the power of maps in Java, enabling efficient data storage, retrieval, transformation, and configuration management. By mastering put, developers can navigate the complex landscape of key-value relationships with ease and efficiency.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: A Deep Dive into the put Method in Java Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!