The Current Map Of Israel: A Complex Landscape Of Borders And Territories
The Current Map of Israel: A Complex Landscape of Borders and Territories
Related Articles: The Current Map of Israel: A Complex Landscape of Borders and Territories
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Current Map of Israel: A Complex Landscape of Borders and Territories. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Current Map of Israel: A Complex Landscape of Borders and Territories

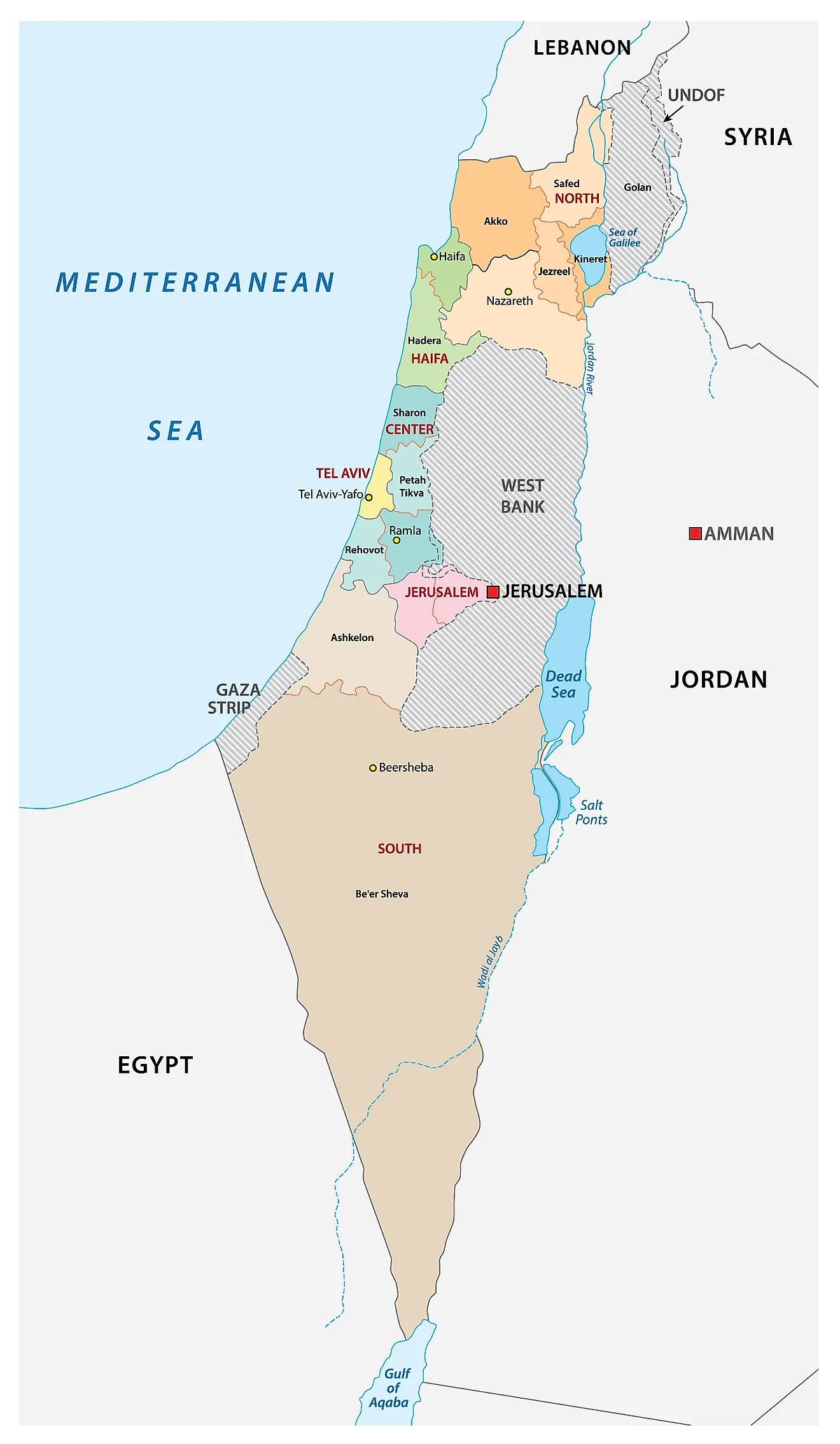
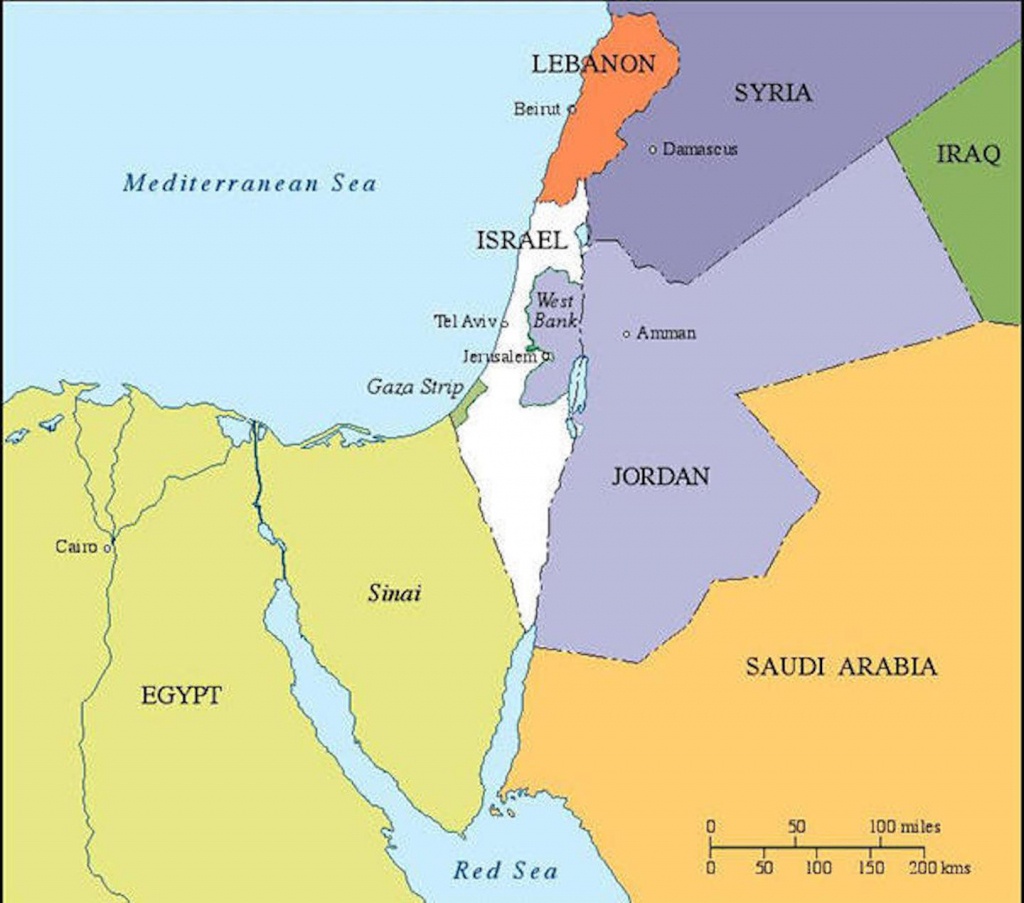
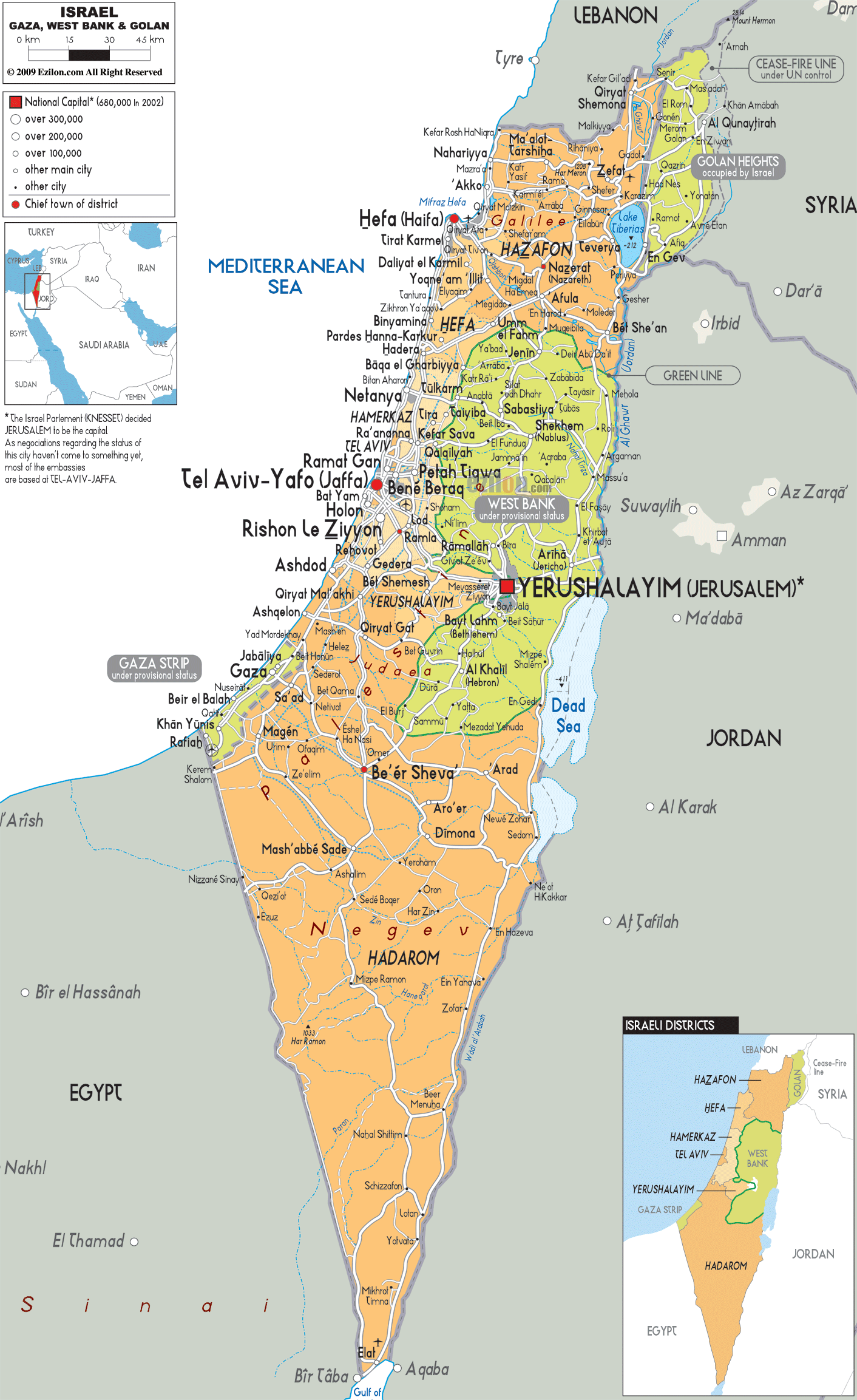
The current map of Israel is a complex and ever-evolving entity, reflecting a history of conflict, negotiations, and political complexities. Understanding its current configuration requires navigating a multifaceted landscape of borders, territories, and international disputes. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the current map of Israel, highlighting its key features, historical context, and ongoing challenges.
The Core of the State: Pre-1967 Borders and the West Bank
The State of Israel was established in 1948, following the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine. This plan divided the territory into two states, one Jewish and one Arab. However, the plan was rejected by the Arab leadership, leading to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. As a result, Israel emerged with a territory larger than initially envisioned, incorporating areas that were not initially assigned to it under the UN plan.
Israel’s pre-1967 borders, also known as the Green Line, represent the boundaries of the state as they existed before the Six-Day War in 1967. This line is generally recognized internationally as the basis for a future two-state solution, with Israel and a Palestinian state coexisting side-by-side.
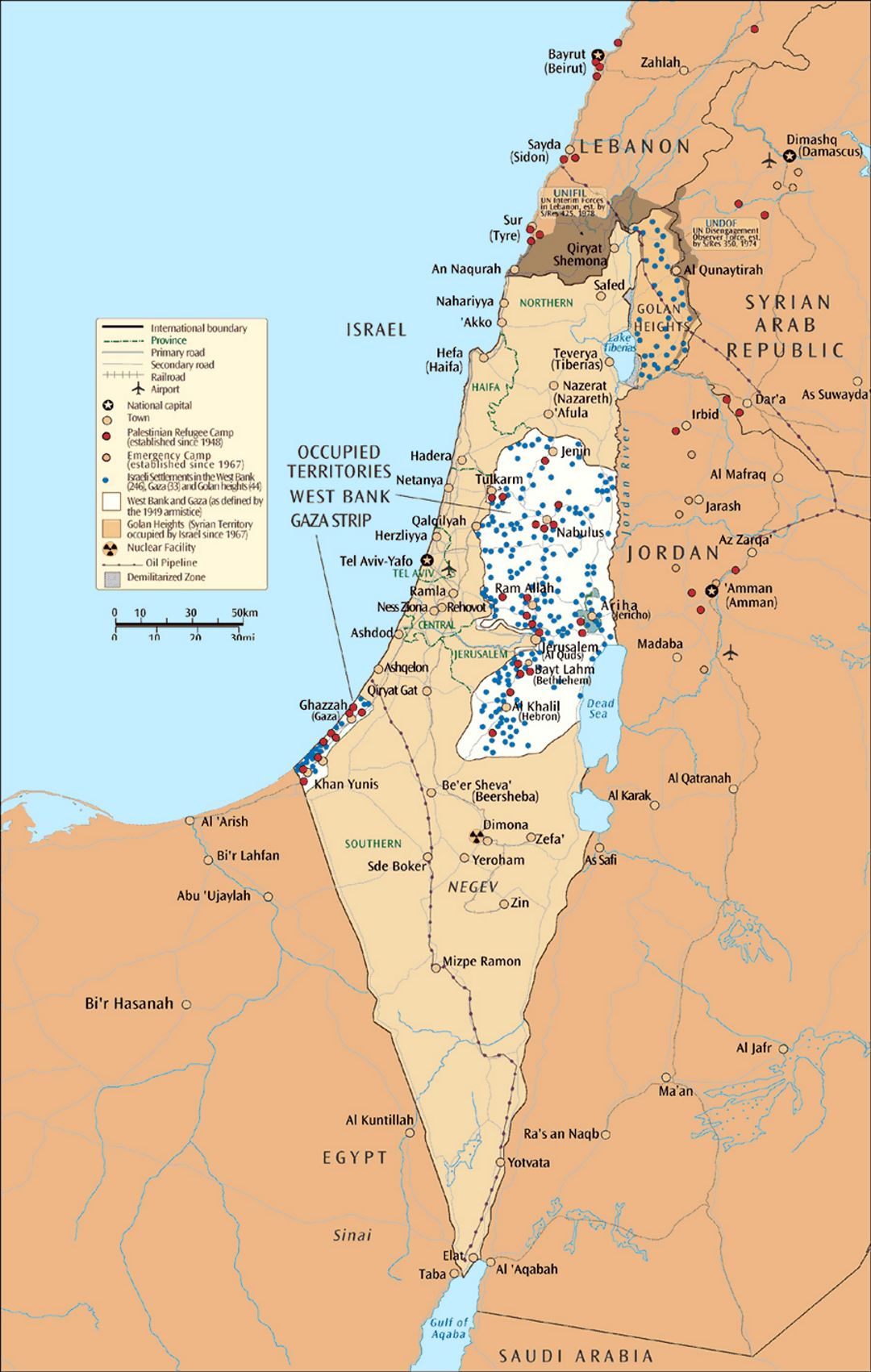
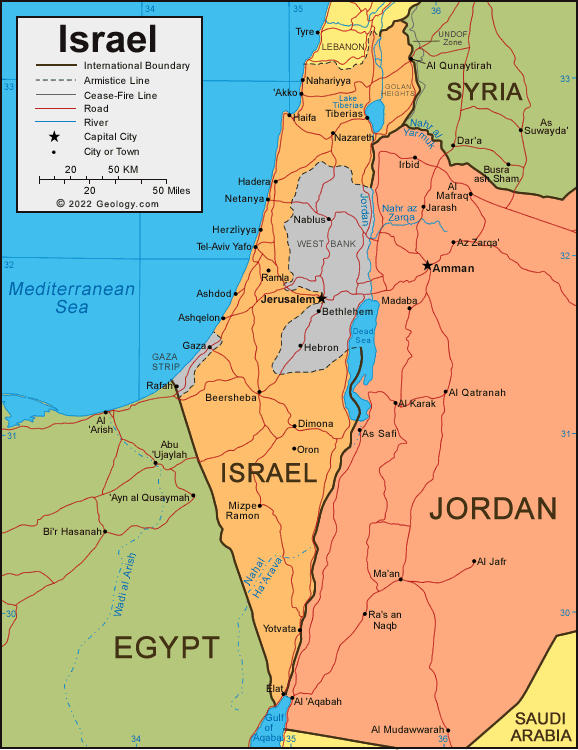
The West Bank, captured by Israel in the Six-Day War, lies beyond the Green Line. This territory is home to a significant Palestinian population and is claimed by both Israel and the Palestinians. The status of the West Bank remains a central point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Israel has established settlements in the West Bank, which are considered illegal under international law, further complicating the situation.
The Gaza Strip: A Separate Entity
The Gaza Strip, another territory captured by Israel in the Six-Day War, is located on the Mediterranean coast. Unlike the West Bank, the Gaza Strip is largely controlled by Hamas, an Islamist group that has fought multiple wars with Israel. The Gaza Strip is densely populated and faces significant humanitarian challenges, including economic hardship and a blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt.
The Golan Heights: A Disputed Territory
The Golan Heights, a strategically important plateau overlooking Israel, was captured from Syria in the Six-Day War. Israel annexed the Golan Heights in 1981, a move not recognized internationally. Syria continues to claim sovereignty over the Golan Heights, and the issue remains a source of tension between the two countries.
The Importance of the Current Map
The current map of Israel is a critical factor in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and regional stability. It represents a complex interplay of historical events, political decisions, and international agreements. Understanding the current map is crucial for comprehending the challenges facing the region and for navigating the complexities of the ongoing peace process.
Challenges and Perspectives
The current map of Israel is a source of ongoing debate and contention. Key challenges include:
- The status of the West Bank: The future of the West Bank remains uncertain, with differing visions for its future among Israelis and Palestinians.
- The Gaza Strip: The ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas in the Gaza Strip poses a significant humanitarian and security challenge.
- The Golan Heights: The annexation of the Golan Heights by Israel remains a contentious issue, raising concerns about international law and regional stability.
- The two-state solution: The viability of a two-state solution, with Israel and a Palestinian state coexisting peacefully, is a subject of ongoing debate and negotiation.
FAQs
Q: What are the current borders of Israel?
A: The current borders of Israel are contested and subject to ongoing negotiations. The pre-1967 borders, known as the Green Line, are generally recognized internationally as the basis for a future two-state solution. However, Israel controls territories beyond the Green Line, including the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights.
Q: What is the status of the West Bank?
A: The status of the West Bank is a key point of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It is claimed by both Israel and the Palestinians, and Israel’s settlement activities in the territory are considered illegal under international law.
Q: What is the situation in the Gaza Strip?
A: The Gaza Strip is controlled by Hamas, an Islamist group that has fought multiple wars with Israel. The territory faces significant humanitarian challenges, including economic hardship and a blockade imposed by Israel and Egypt.
Q: What is the international consensus on the Golan Heights?
A: The international community does not recognize Israel’s annexation of the Golan Heights. Syria continues to claim sovereignty over the territory.
Q: What are the main obstacles to a two-state solution?
A: Obstacles to a two-state solution include:
- Israeli settlements in the West Bank
- The status of Jerusalem
- The issue of Palestinian refugees
- Security concerns
Tips
- Study the history: Understanding the historical context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is essential for comprehending the current map.
- Follow the news: Stay informed about current events in the region, including negotiations and developments related to the borders and territories.
- Engage in respectful dialogue: Engage in constructive conversations about the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, acknowledging different perspectives and seeking common ground.
Conclusion
The current map of Israel is a complex and dynamic landscape that reflects a long and tumultuous history. The ongoing challenges related to borders, territories, and political disputes highlight the need for continued dialogue, compromise, and a commitment to finding a peaceful resolution. Understanding the current map is crucial for comprehending the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and for navigating the path towards a lasting peace.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Current Map of Israel: A Complex Landscape of Borders and Territories. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!