The Ivory Coast: A Geographic And Historical Perspective
The Ivory Coast: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
Related Articles: The Ivory Coast: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ivory Coast: A Geographic and Historical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ivory Coast: A Geographic and Historical Perspective
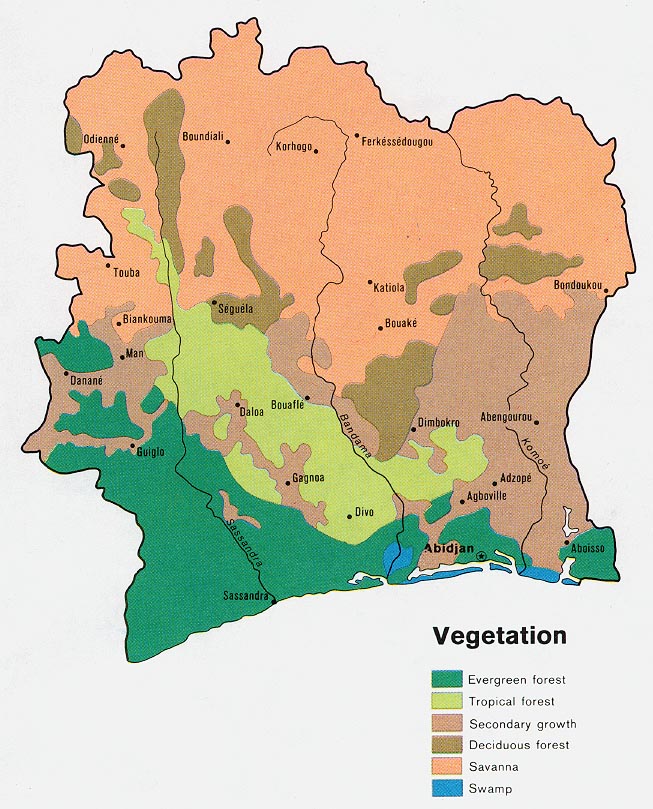
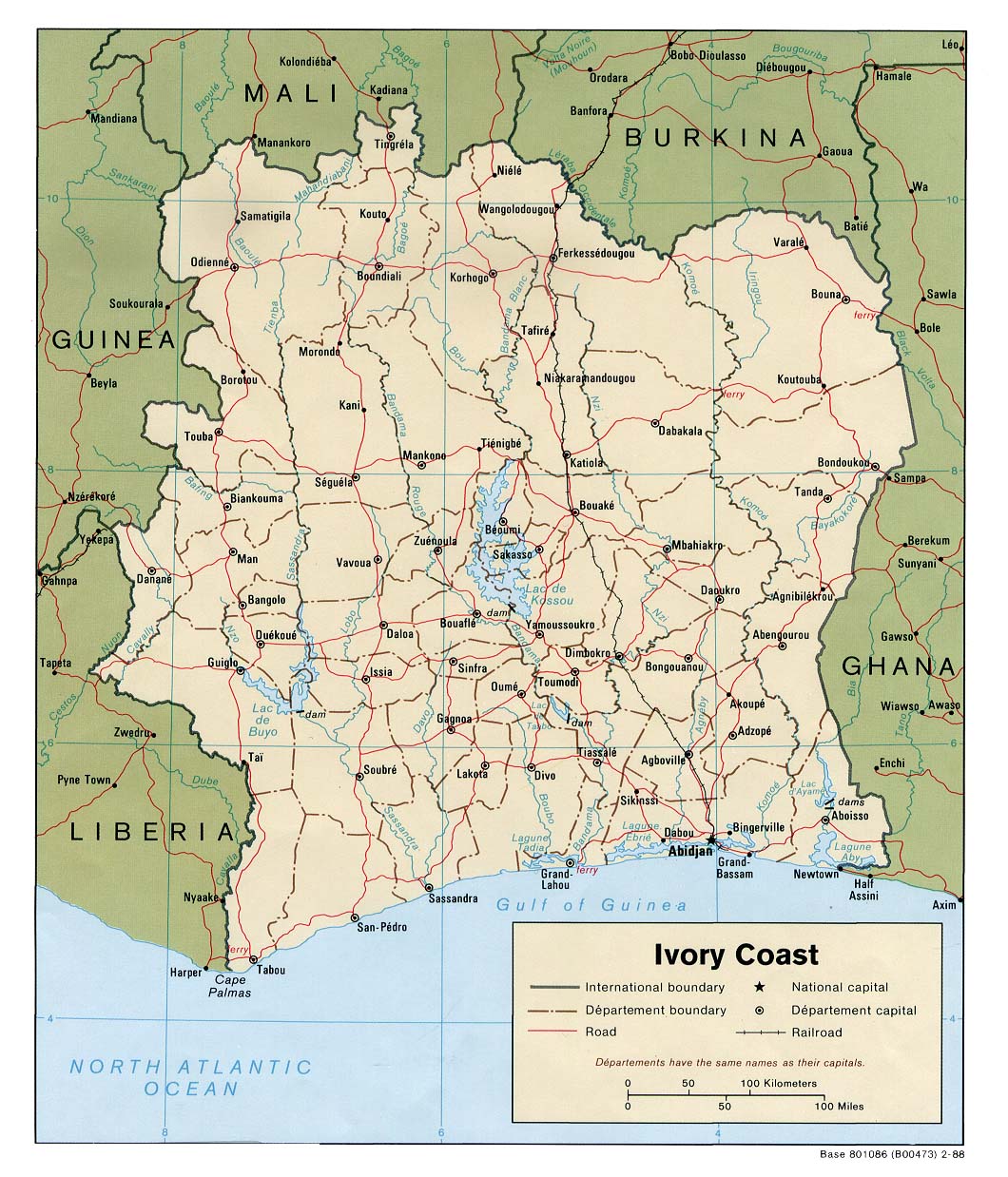
The Ivory Coast, officially the Republic of Côte d’Ivoire, is a West African nation situated on the southern edge of the continent. Its unique geographic location and rich history have shaped its diverse landscape, cultural tapestry, and economic potential. This article delves into the intricacies of the Ivory Coast, exploring its geography, history, culture, and current socio-economic landscape.
Geography: A Mosaic of Landscapes
The Ivory Coast is characterized by a varied topography, encompassing coastal plains, rolling hills, and the sprawling savanna of the north. The nation’s coastline stretches for over 500 kilometers along the Gulf of Guinea, offering access to a network of lagoons and estuaries.
- Coastal Plains: The southern portion of the country is dominated by fertile coastal plains, a region renowned for its rich agricultural output, particularly cocoa, coffee, and rubber.
- Rolling Hills: Moving inland, the landscape transitions into rolling hills, where the iconic Mount Nimba, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, rises to a height of 1,752 meters.
- Savanna: The northern region is characterized by vast savanna grasslands, a stark contrast to the lush greenery of the south. This region is home to diverse wildlife, including elephants, lions, and leopards.
Hydrography: A Network of Rivers and Lagoons
The Ivory Coast is blessed with a network of rivers and lagoons that play a crucial role in its economy and ecosystem. The most significant river is the Comoé River, which flows through the center of the country, providing essential water resources for agriculture and transportation. The nation’s numerous lagoons, connected to the Atlantic Ocean by narrow channels, offer opportunities for fishing and transportation.
Climate: Tropical Diversity
The Ivory Coast enjoys a tropical climate, characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons. The southern region experiences high humidity and heavy rainfall throughout the year, while the northern savanna is characterized by a more pronounced dry season. This variation in climate has a significant impact on the country’s agricultural production and biodiversity.
History: From Ancient Kingdoms to Modern Nationhood
The history of the Ivory Coast is a rich tapestry woven from the threads of ancient kingdoms, European colonization, and the struggle for independence.
- Ancient Kingdoms: Prior to European arrival, the region was home to various powerful kingdoms, including the Baule, the Agni, and the Senufo. These kingdoms developed sophisticated social structures, artistic traditions, and trade networks.
- European Colonization: In the late 19th century, European powers, notably France, began to exert their influence in the region. The Ivory Coast became a French colony in 1893, and its economy was transformed by the introduction of cash crops like cocoa and coffee.
- Independence: The Ivory Coast gained independence from France in 1960. The first president, Félix Houphouët-Boigny, ruled for over 30 years, implementing policies that fostered economic growth and stability. However, the nation experienced political turmoil and economic decline following his death in 1993.
- Recent History: The Ivory Coast has undergone a period of instability and political unrest in recent decades. The country experienced a civil war in 2002, which lasted for over a decade and left a lasting impact on its socio-economic landscape. In recent years, the nation has made strides towards reconciliation and economic recovery, but challenges remain.
Culture: A Blend of Traditions and Modernity
The Ivory Coast boasts a vibrant and diverse culture, shaped by its rich history, diverse ethnic groups, and geographic location.
- Ethnic Diversity: The country is home to over 60 distinct ethnic groups, each with its own language, traditions, and customs. The largest groups include the Akan, the Baoule, and the Senufo.
- Art and Music: The Ivory Coast is renowned for its vibrant artistic traditions, particularly in sculpture, textiles, and music. Traditional music, characterized by its rhythmic complexity and use of percussion instruments, plays a central role in social life.
- Religion: The Ivory Coast is a predominantly religious country, with a significant majority adhering to Christianity and Islam. Traditional animistic beliefs also play a role in the cultural landscape.
Economy: From Agriculture to Industry
The Ivory Coast’s economy has historically been heavily reliant on agriculture, particularly cocoa production, which has earned it the nickname "the world’s cocoa capital." However, the nation has made significant strides in diversifying its economy, expanding into sectors like manufacturing, tourism, and services.
- Agriculture: Cocoa, coffee, and rubber remain crucial contributors to the Ivory Coast’s economy, employing a large portion of the workforce. However, the sector faces challenges related to climate change, disease, and volatile commodity prices.
- Manufacturing: The Ivory Coast has made progress in developing its manufacturing sector, with industries such as textiles, food processing, and construction gaining momentum.
- Tourism: The country’s diverse landscapes, rich culture, and burgeoning infrastructure have attracted growing numbers of tourists, particularly from neighboring countries.
- Services: The service sector is increasingly contributing to the Ivory Coast’s economy, with significant growth in areas like finance, telecommunications, and retail.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its economic progress, the Ivory Coast faces several challenges, including:
- Poverty: Poverty remains a significant issue, with a large portion of the population living below the poverty line.
- Inequality: Income inequality persists, with a significant gap between the wealthy elite and the majority of the population.
- Corruption: Corruption is a pervasive issue, hindering economic development and undermining public trust in institutions.
- Climate Change: The Ivory Coast is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including droughts, floods, and rising sea levels, which threaten its agricultural sector and coastal communities.
Conclusion: A Nation on the Move
The Ivory Coast is a nation with a rich history, diverse culture, and significant economic potential. Despite the challenges it faces, the country has made notable progress in recent years towards stability, economic growth, and social development. Its geographic location, abundant natural resources, and vibrant culture offer a foundation for continued growth and prosperity. As the nation navigates the complexities of the 21st century, its ability to harness its resources, address its challenges, and foster inclusive growth will determine its future trajectory.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ivory Coast: A Geographic and Historical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!