Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Zones: A Guide To Navigating A Geologically Active Nation
Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Zones: A Guide to Navigating a Geologically Active Nation
Related Articles: Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Zones: A Guide to Navigating a Geologically Active Nation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Zones: A Guide to Navigating a Geologically Active Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Zones: A Guide to Navigating a Geologically Active Nation

Indonesia, an archipelago nation sprawling across Southeast Asia and Oceania, is renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty. However, this beauty is intertwined with a stark reality: Indonesia sits atop a complex network of tectonic plates, making it one of the most seismically active regions on Earth. This geological dynamism presents both challenges and opportunities for the nation, requiring a deep understanding of its seismic zones to mitigate risks and harness the potential of geothermal energy.
The Tectonic Tapestry of Indonesia:
Indonesia’s location at the confluence of three major tectonic plates – the Eurasian, Indo-Australian, and Pacific plates – creates a dynamic and volatile geological landscape. These plates constantly interact, pushing, pulling, and grinding against each other, generating immense pressure that manifests in the form of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountains and trenches.
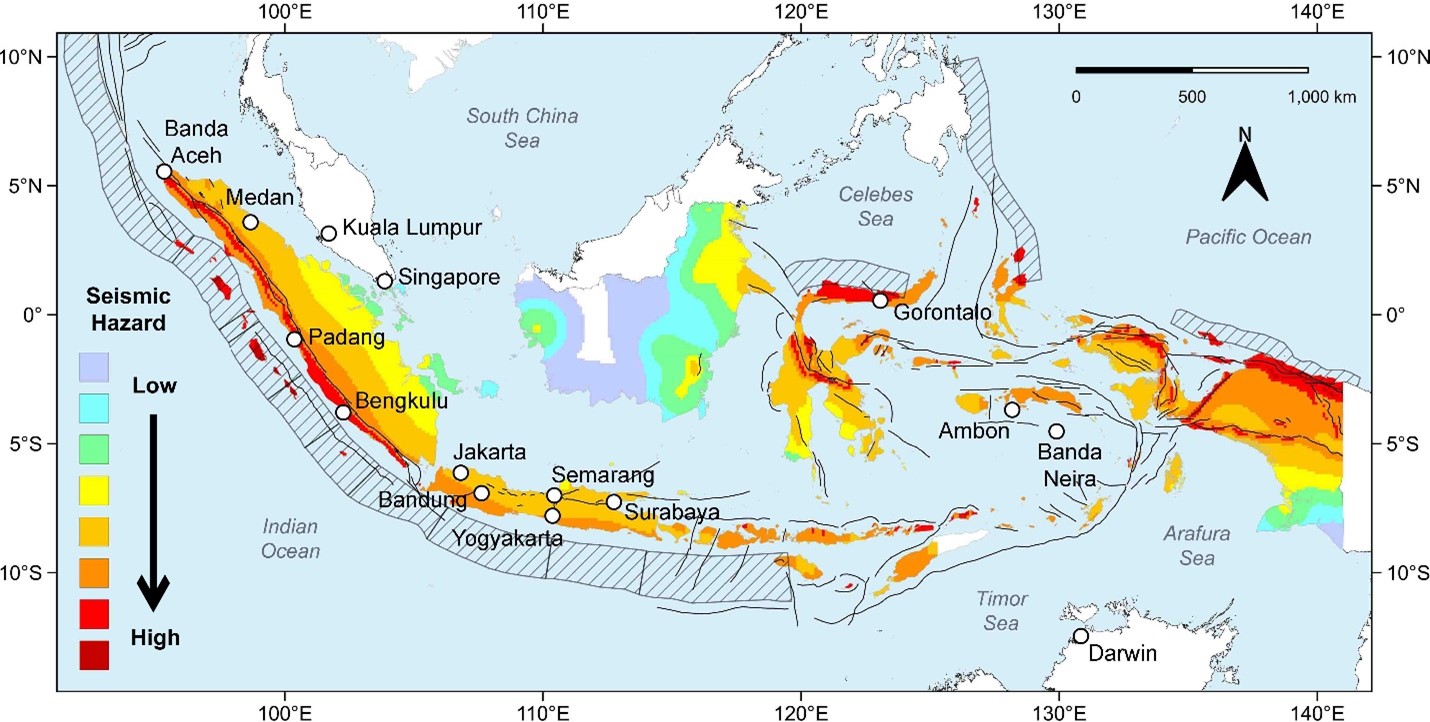
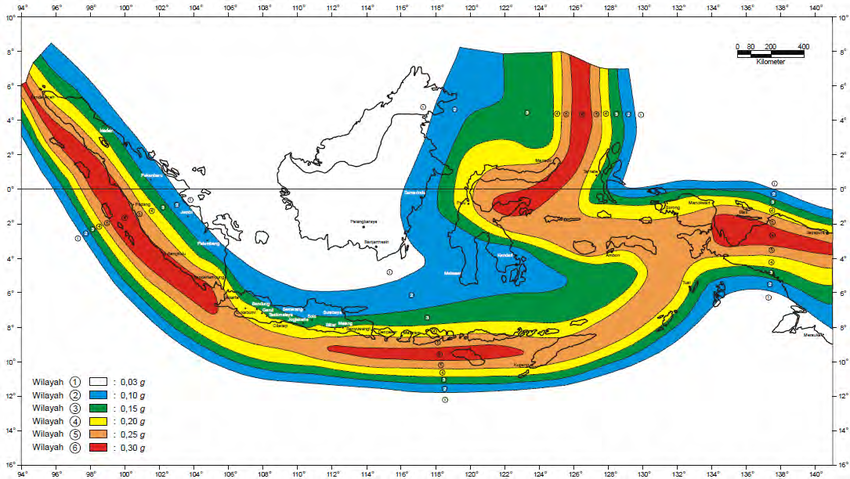
Seismic Zones: A Framework for Understanding Risk:
To assess and manage the seismic hazards, Indonesia has developed a seismic zoning map. This map categorizes the country into different zones based on their susceptibility to earthquakes. The zones are designated with Roman numerals, with higher numbers indicating higher seismic activity.
Zone I: Low Seismic Risk
Zone I encompasses areas with minimal seismic activity, characterized by stable geological formations and a low likelihood of experiencing significant earthquakes. These zones are typically found in the interior regions of the country, far from the active plate boundaries.
Zone II: Moderate Seismic Risk
Zone II represents areas with moderate seismic activity, experiencing occasional earthquakes of moderate intensity. These zones are usually situated in proximity to the major fault lines but are not directly on the plate boundaries.
Zone III: High Seismic Risk
Zone III signifies areas with high seismic activity, frequently experiencing earthquakes of varying intensities. These zones are located directly on the active plate boundaries, where the tectonic plates collide or slide past each other.
Zone IV: Very High Seismic Risk
Zone IV encompasses areas with the highest seismic activity, characterized by frequent and intense earthquakes. These zones are situated in the most active tectonic zones, where the plates interact with the greatest force.
The Importance of Seismic Zoning Maps:
The seismic zoning map serves as a crucial tool for various stakeholders:
- Government Agencies: The map informs the development of building codes and disaster management plans, ensuring structures are designed to withstand seismic forces and facilitating efficient emergency response strategies.
- Infrastructure Developers: The map guides the construction of critical infrastructure, such as bridges, dams, and power plants, ensuring their resilience to earthquakes and minimizing potential damage.
- Urban Planners: The map helps identify high-risk areas for urbanization, promoting responsible land use practices and minimizing the impact of seismic events on population centers.
- Insurance Companies: The map assists in assessing earthquake risks and developing appropriate insurance policies for individuals and businesses.
- Researchers and Scientists: The map provides valuable data for understanding the dynamics of plate tectonics and predicting future seismic activity, contributing to scientific research and disaster preparedness.
Beyond Risk: Harnessing the Power of Geothermal Energy:
While Indonesia’s seismic activity poses challenges, it also presents an opportunity: the abundance of geothermal energy. The heat generated by the Earth’s internal processes, particularly in areas of high seismic activity, can be harnessed to generate clean and renewable energy.
Indonesia is actively developing its geothermal resources, leveraging its seismic zones to power homes and industries. This sustainable energy source offers a significant advantage, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of energy production.
FAQs on Indonesia’s Seismic Zones:
Q: Are there specific areas in Indonesia that are most vulnerable to earthquakes?
A: The areas located on or near the major plate boundaries, particularly in Sumatra, Java, and Papua, are the most vulnerable to earthquakes. These regions fall under Zone IV on the seismic zoning map, indicating the highest seismic risk.
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Indonesia?
A: Indonesia experiences numerous earthquakes every year, ranging from minor tremors to major events. The frequency and intensity of these events vary depending on the specific location and the interaction of the tectonic plates.
Q: What measures are in place to mitigate the impact of earthquakes in Indonesia?
A: Indonesia has implemented various measures to mitigate the impact of earthquakes, including:
- Building Codes: Strict building codes are enforced to ensure structures are designed to withstand seismic forces.
- Disaster Preparedness Programs: Public awareness campaigns and training programs are conducted to educate the population on earthquake preparedness.
- Early Warning Systems: Advanced earthquake early warning systems are being developed to provide timely alerts to the public and emergency responders.
- Infrastructure Reinforcement: Existing infrastructure is being reinforced to enhance its resilience to seismic events.
Q: What are the long-term implications of Indonesia’s seismic activity?
A: Indonesia’s seismic activity has significant long-term implications:
- Landslide Risk: Earthquakes can trigger landslides, posing a threat to lives and infrastructure.
- Tsunami Risk: Earthquakes in coastal areas can generate tsunamis, causing widespread devastation.
- Volcanic Activity: Seismic activity often accompanies volcanic eruptions, increasing the risk of volcanic hazards.
- Economic Impact: Earthquakes can disrupt economic activities, causing significant damage to infrastructure and businesses.
Tips for Living in a Seismic Zone:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about earthquake preparedness and safety measures.
- Secure Your Home: Secure heavy objects and furniture to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Have an Emergency Plan: Develop a family emergency plan, including evacuation routes and communication strategies.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit containing essential supplies, such as water, food, first aid, and a flashlight.
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Pay attention to your environment and be alert for signs of seismic activity.
Conclusion:
Indonesia’s seismic zoning map is a valuable tool for understanding and managing the risks associated with its dynamic geological landscape. By recognizing the potential dangers and implementing appropriate measures, Indonesia can mitigate the impact of earthquakes and harness the opportunities presented by its geothermal resources. This comprehensive approach ensures a future where the nation can thrive despite the challenges posed by its seismic activity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Indonesia’s Seismic Zones: A Guide to Navigating a Geologically Active Nation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!